Blog Grid
- Home
- Blog Grid
Crypto & Web3 Projects

Crypto & Web3 Projects
Crypto and Web3 projects are transforming how we use the internet by giving people more control over their money, data, and digital identity. Instead of relying on banks or big tech companies, these projects use blockchain technology to let users interact directly, whether it’s sending money, owning digital assets like NFTs, or using apps without giving up privacy. It’s all about building a more open, secure, and user-focused internet for the future.
Here are some websites where you can earn money by simply using your internet — and some of them are completely free to use!
- Join Intract Quest – discover top Web3 projects, complete simple tasks, and earn rewards like tokens & NFTs! 🎯
Join @ https://bit.ly/qstintrctgrk
Intract #Web3 #CryptoRewards #LearnAndEarn #CryptoCommunity #BlockchainJourney - 🔥 Hurry up! GOLD STRIKE is exploding on Telegram! 🚀
Spin, score, and earn your share of the airdrop!
🏆 Don’t miss out—PLAY NOW!
Join @ https://bit.ly/goldstriker
💎 Play. Win. Earn. It’s that simple!
CryptoGaming #EarnWhileYouPlay #FreeTON #TelegramGames
- Rent Out Your Unused Internet and Earn Money
Join @ https://bit.ly/grassiogrk
Download the desktop app for boosted rewards and start earning today !
- Earn Free Yohi & USDT in the Game!
Join @ https://bit.ly/YohiCrypto
Join Yohi and earn airdrops and USDT with me.🤩💰
 DDAI Network – New DePIN from Solana
DDAI Network – New DePIN from Solana
The first AI-powered DePin on Solana. How to start:
How to start:  Follow the link
Follow the link
Join @ https://bit.ly/ddaispace
Monetize your unused internet using AI!!

Maximizing the Potential of Cloud Infrastructure: Strategies for Success
Maximizing the Potential of Cloud Infrastructure in today’s ever-changing world of digital marketing, nothing remains constant. Innovations are constantly being introduced, becoming integral parts of the business, cloud computing is also one such innovation. With cloud computing, you get incredible benefits of unparalleled scalability, unmatched flexibility, and iron-clad security. Compared to other traditional systems cloud computing helps businesses effortlessly adapt advanced technologies, making them more accessible and easier to support.
Getting the full essence of cloud infrastructure requires strategic planning, execution, and continuous optimization. Allowing your business to harness its capabilities together to effectively propel itself towards growth in the digital age.

Maximizing the Potential of Cloud Infrastructure
What is Cloud Infrastructure?
Cloud infrastructure is the first step in modern computing. it’s all about how businesses handle their IT resources and deliver their services. To understand cloud infrastructure, we need to know and understand what is cloud computing and how it works
Cloud infrastructure is the hardware and software that make cloud computing possible. Cloud computing means using the internet to get access to computing stuff like networks, servers, storage, apps, and services whenever you need them.
What are the main parts of cloud infrastructure?
The main parts of cloud infrastructure are
- Virtualization: This makes virtual copies of computer resources, so they are used efficiently and can grow and skim as needed.
- Networking: It makes sure everything stays connected so data can move smoothly between users and cloud services.
- Storage: It’s like a big, flexible storage space where data is kept safely and can be easily accessed
- Compute: This is the power to run programs and process data, all happening in virtual machines
The evolution of cloud infrastructure started around 2000 when companies began to think about using computing like a utility, just like electricity, Amazon took off with this idea in 2006 when they launched Amazon EC2, which let people rent virtual servers and storage whenever they needed.
Since then, cloud technology has grown fast. We now have things like Platform as a Service ( PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS), which give developers and businesses more ways to use and build applications on the cloud.
Types of Cloud Infrastructure:
There are a variety of cloud infrastructures that cater to different needs. The following are the most frequent kinds:
Public Cloud – This is the internet-based shared space that businesses rent out. It is an excellent option for small businesses or startups for a few factors. First and foremost, businesses only pay for what they utilize, which is ideal for businesses with low financial resources.
Private Cloud – I believe that one day I would own one complete cloud infrastructure just for me and my staff. It is ideal for large corporations or organizations with excellent safety measures.
Hybrid Cloud – this cloud combines the advantages of both public and private environments. It is an excellent resource if some materials are better placed in a private environment while others are better used in the public domain.
Advantages of cloud infrastructure
Understanding cloud infrastructure means learning the basic ideas, how it started, and the different ways it’s used today. When businesses use cloud tech smartly, they can do things more easily, grow quickly, and work more efficiently.
Cloud infrastructure is super important for businesses now. It gives lots of good stuff like making things run smoother, growing faster, and keeping things safe. Knowing these benefits helps us see why so many businesses are switching to cloud solutions.
Scalability and Flexibility
The biggest advantage of cloud infrastructure is how easily it can grow and change. Unlike old systems where getting bigger meant lots of time and money for new equipment, the cloud lets businesses update their tech as needed. This means dealing with sudden user growth or growing seamlessly.
Cloud providers offer resources that can grow and shrink. Such as virtual machines and storage. So, if you need more power for busy times or extra space for larger projects, cloud tech can do that easily.
Also, cloud systems can adjust resources based on how busy things are. This helps to manage everything smoothly and reduces costs
Cost-effectiveness
Another interesting benefit of cloud infrastructure is cost efficiency. Cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go or subscription-based model, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they use. This eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, making cloud computing particularly attractive for start-ups and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Also, cloud providers offer cost-effective pricing mechanisms to provide cost-effective pricing strategies to accurately calculate costs, reduce costs for long-term commitments, and cost estimates With these tools and services with implementation, companies can optimize costs, allocate resources more efficiently, and run their businesses more cost-effectively.
Additionally, cloud infrastructure reduces the operational costs associated with maintenance, upgrades, and support, as these responsibilities are usually handled by a cloud provider this allows organizations to divert resources and focus on core business objectives rather than IT management services.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating cloud services with your current systems is an important part of using cloud technology well. Many companies have already spent a lot of money on their own systems and software, so it’s crucial to make sure everything works together smoothly when you start using cloud services.
One way to do this is by using hybrid cloud solutions. This means you keep some of your stuff on your own systems and use cloud services for things like getting more space when you need it or being able to change things easily. Hybrid cloud setups help connect your own systems with the cloud so they can talk to each other and share information without any problems.
You can also use special tools like APIs (which help different software talk to each other), middleware (which helps connect different systems), and integration platforms. These tools make it easier for your systems to work together, whether they’re in the cloud or on your own servers. They make sure everything runs smoothly and your data stays consistent across all your systems.
Performance optimisation
Optimizing how well your cloud system works is really important to make sure you get the most out of it in terms of getting things done, using resources wisely, and saving money. Cloud systems have lots of options and ways to make them work better so you can do more without spending too much.
One way to make sure your cloud system performs well is by using the right amount of resources. This means giving your system enough power and space based on what you’re doing, so you don’t waste resources or run out when you need them. Cloud providers have tools to help you keep an eye on how your system is doing and make changes to save money and make things work faster.
Another way to improve performance is by using automation tools. These tools help you do things automatically without needing someone to do them manually every time. This makes things run smoother, saves time, and makes sure everything works the same way every time.
In summary, using cloud systems well means planning carefully, working together, and doing things in a smart way. By moving to the cloud, connecting with your existing systems, and making sure everything runs smoothly, you can use technology better, be more flexible, and stay competitive in today’s digital world.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are fancy ways of saying smart computer programs that can learn and make decisions on their own. These technologies are changing how companies use data, automate work, and make choices.
Cloud infrastructure, which is like a giant computer system on the internet, is a perfect place for AI and ML. It’s big enough to handle lots of data and powerful enough to run these smart programs.
When AI and ML are combined with cloud systems, companies can do cool things like finding important information in big piles of data. For example, they can train these smart programs to spot trends, predict what might happen next, and make things run smoother in areas like money, health, selling stuff, and making things.
Using AI and ML in the cloud also means companies can make computers do boring tasks automatically, like answering customer questions or finding problems before they happen. This saves time and helps businesses work better.
From chatbots that talk to customers to systems that predict when machines need fixing, the possibilities with AI and ML in the cloud are endless. It’s like having super-smart helpers that make everything easier and faster.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The Internet of Things (Io) is a big network of connected devices, sensors, and systems that talk to each other and share information over the Internet. Cloud infrastructure is like a big storage and processing center in the sky that helps manage this information
When we integrate IoT with cloud infrastructure, it means we connect all these smart devices and sensors to the cloud. this connection let us do things like getting relevant information from these devices, controlling them from afar, and making our processes work better.
For example, in big developed cities, we can use IoT sensors in things like traffic lights and buildings to collect data on how people move around, the air quality, and how much energy we are using. Then, we send this data to the cloud where it’s analyzed. This helps city planners make better decisions about things like where to put new roads or parks, and how to make the city more eco-friendly
Cloud-based IoT platforms are also great because they can grow and change easily. This is important because we’re using more and more smart devices every day in different industries like healthcare, farming, and making stuff. So, having a flexible system that can handle all this new tech is super helpful!
Blockchain Integration
Blockchain Technology best known as the Technology behind cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, is increasingly being used to enhance the security and transparency of cloud infrastructure. Blockchain Technology can help organizations Secure data valid and processes and mitigation risks associated with a centralized system.
In cloud infrastructure, blockchain integration can be utilized in various ways, such as securing data storage and transmission, verifying the integrity of software and firmware and updates, and enabling secure peer-to-peer transactions. For example, blockchain-based identity management systems can provide a more secure and efficient way to manage user authentication and access control in cloud environments.
Moreover, blockchain technology can enhance the transparency and auditability of cloud infrastructure by providing a tamper-proof record of all transactions and changes made to data and configurations. This can help organizations demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements, enhance trust among stakeholders, and improve accountability in cloud-based systems.
In conclusion, leveraging advanced cloud services such as AI and ML, IoT integration, and blockchain technology offers organizations a multitude of opportunities to innovate, optimize processes, and enhance security in their cloud infrastructure. By harnessing the power of these technologies, organizations can unlock new insights, improve decision-making, and stay ahead of the curve in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Ensuring compliance and governance in cloud infrastructure is paramount for organizations operating in today’s regulatory environment. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services for data storage, processing, and management, it’s essential to prioritize adherence to industry standards and regulations, maintain data integrity and privacy, and effectively manage risks associated with cloud infrastructure.
Regulatory Compliance
Following rules and laws is very important when managing a cloud system well. There are different rules like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC 2 that have strict requirements for handling data and keeping it safe.
First, organisation need to know what rules they must follow based on their industry, where they are, and what kind of data they use. For example, healthcare groups must follow HIPAA To protect patient information, while businesses dealing with payment cards need to be strict with PCI DSS rules.
Providers of the cloud also play a big role in following these rules. They often help certificates showing their follow the rules correctly. Organizations should choose providers with good complain programs and clear audits.
Inside the organization, clear rules and plans are needed to keep following the rules. This includes who can access the data, how data is kept safe, how long data is kept and what to do if there is a security problem.
Regular checks and evaluations are important to see if everything is following the rules properly. These checks help find any problems and fix them so that data stays protected and legal requirements are met.
Data Governance
Data governance is about keeping data safe, accurate, and following rules, especially in cloud setups. it is all about the rules, processes, and tools that control how data is collected, stored, used, and deleted.
In a cloud system strong data governance means protecting sensitive data stopping unauthorized access, and following the rules. This includes using tools to classify data, encrypt it control who can access it and prevent data leaks.
Organizations also need clear rules on how data is accessed, shared, and used to avoid breaches. Data governance should include checks, monitoring, and rules to make sure everyone follows the data rules and meets legal requirements.
Risk management
Managing risk in cloud infrastructure is very important for ensuring the safety and reliability of business operations. Cloud introduces various risks such as data breaches, service interruption, vendor dependency, and regulatory violations, which can lead to significant, financial, reputational, and legal consequences
To effectively handle these risks, organizations need to conduct risk assessments to identify potential threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts on their cloud infrastructure. This involves analyzing the security measures of cloud service providers, examining data protection controls, and pinpointing the weak spots in the infrastructure.
once risks are identified organizations should start to develop risk mitigation strategies and backup plans to address vulnerability and decrease the chances of adverse events. This will also include implementing security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection, and vulnerability scanners as well as backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure business continuity in case of destruction or data loss.
Once risks are identified, organizations should develop risk mitigation strategies and backup plans to address vulnerabilities and minimize the chances of adverse events. This may include implementing security tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and vulnerability scanners, as well as establishing backup and disaster recovery plans to ensure business continuity in case of disruptions or data loss.
Moreover, organizations should regularly monitor and evaluate their cloud infrastructure for emerging threats and vulnerabilities, and update their risk management strategies accordingly. Staying informed about security updates, patches, and best practices recommended by cloud providers and experts is crucial for maintaining a secure cloud environment.
In precise, ensuring compliance and governance in cloud infrastructure requires a comprehensive approach that includes regulatory adherence, data governance, and risk management. By prioritizing compliance with industry standards, implementing strong data governance practices, and effectively managing risks, organizations can mitigate potential threats, safeguard sensitive information, and uphold the security and reliability of their cloud setups.
Implementing cloud infrastructure effectively necessitates meticulous planning, collaboration, and execution. By utilizing cloud migration strategies, integrating with existing systems, and optimizing performance, organizations can harness the full potential of cloud computing, driving innovation, agility, and competitiveness in the digital era.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

Cyber Security Best Practices for Businesses: Protecting Your Assets in the Digital Age
The Internet is increasingly becoming a popular environment for business and investing in it requires proper measures taken to safeguard your assets.
Cyber Security Best Practices
Indeed, proactive measures against cyber-attacks make many firms shut down their operations in the digital age. Financial loss and loss of intellectual property, cyber terrorism, ransomwear, phishing, malware and data theft. Emails, credit card details, and even customer lists, intellectual property, even lists containing employee information are all vulnerable to hacking by someone interested. That is why there are hackers out there, always robbing or invading your treasures.
Cyber-criminals are on the prowl, and regardless of the scale of the business or the specific type of digital property, cybersecurity must be taken seriously by all organizations. To this end, this article focuses on the different threats, the importance of cybersecurity, preventing, measures, tools, and guidance that one ought to consider for the enhancement of cybersecurity and the shield of properties against internet vices.

This is the procedure that aims at stopping other people from accessing networks, technological devices, and even personal data without permission. Cybersecurity is also required to avoid loss in data due to cyber-terrorism for each individual, businessman or a governmental organization. The importance of cybersecurity has been fueled by the current advancement of technology in the society. It encompasses a host of protection measures to prevent the loss of data and deter potential cyber threats that result in its compromise and unavailability.
In general cybersecurity can be rightly understood that it is a process of minimizing data risks by implementing and applying means and tools that ensure trust in digital environment. In this regard, both cybersecurity and compliance with enhanced and accurate security systems should be high priorities in order to minimize threats of hacked cyber-world incidents and further negative implications of security breakage.
More than ever, it is crucial to protect our personal data and possessions that are stored through digital means.
In the present day, intuitive measures have to be taken to protect your investments from cyber threats. One can safeguard anything that can endanger one’s identity, financial status, or image, including money or other important documents. Some crucial elements of safeguarding assets from cybercriminals are as follows:Some crucial elements of safeguarding assets from cybercriminals are as follows:
Maintaining Financial and Personal Identity
Firstly, identity information and other financial details are the valuable resources that need protection. Due to this, fraudsters are in a position to acquire credit cards and other identity cards, reach various e-shops and even compromise the tax system through tax frauds. This may be due to inadequate password protection or the passwords being easily guessable; it is thus important for you to ensure that you use proper passwords, and where possible change them frequently in a bid to protect your data from such individuals.
First, ensure that your data is safe by protecting your identity through two-factor authentication, and second, ensure that you do not disclose your identity on the internet. However, please read the following tips on how you can protect yourself against financial fraud: Finally, you should never use your credit card or bank account on the internet using public wireless networks and ensure you review your credit card and bank statements for any suspicious activities frequently.
Safeguarding Your Company’s Resources
Everybody knows that being an owner of a business, you must do all that is possible to protect the businesses you own. Whether it is about eating, paying through a credit card, getting to know confidential information or about closing your business, hackers are capable of doing all this. To try to protect the business’ assets, one should set a complex and unique password and employ two-factor authentication. In addition to this, do use firewalls and antivirus software and ensure to update your software routinely to reduce the risks to your network. Training your employees to develop risk awareness and keep away from frauds as well as other risks can also be done.
So, here are the most effective tips to increase the level of cybersecurity sources investment:
To mitigate cybersecurity there are several measures that will be available for application in protecting the company’s assets. This is a process that has components such as firewalls, antivirus, intrusion detection among many others. Now, let us say we are considering cybersecurity, some of the factors that should not be dismissed include cost, convenience, and efficiency. Search for real-time detection or threat and other features, if any, if you are trying to find such solutions.
Regularly backup your data
Without a doubt, this is one of the most effective means to ensure your asset’s safety, following the creation of backup files. One of the best recommendations that you could make as per the best practices in using computers is to always have data backup in the cloud. It is also important that you should frequently run cross checks on your backup in order to enable your data to be retrieved from invasions within the shortest time possible.
To be effective serious incidents require a plan on how to respond to them when they occur.
Cybersecurity is essential for any business, which means they should have cybersecurity strategy for addressing cyber threats. Thus, establish protective and aggressive response measures outlining the steps needed to avoid and manage such occurrences in the future. Here are some things that you need to ensure in your organization: You should consider some factors when it comes to incident response strategy to ensure that it is working effectively as follows:
Following these tips will help you protect your belongings from corrupt individuals.
Types Of Cyber Threats
In the current world, information technology has become widespread, and therefore industries must employ cybersecurity strategies to prevent their data from being compromised. The effects of cyberattacks range from severe personal ramifications on one’s financial, reputational, and personal fronts. This is because the world of cyber threats cannot be left unknown to comprehend the category of risks at the same time learning how to protect the assets of the business from hackers. Typical cyberthreats and preventative measures are listed in the following list:
Malware
Malware is a sort of software designed to harm your computer system and communication system. Trojans, worms, viruses, and malware may form part of what it is. Several scenarios exist through which malware may penetrate a certain system; for instance, when a user opens an email with an unsafe link, downloads infected content or visits a specific website. Malware can be defended by regularly installing antivirus software, updating installed softwares, avoiding clicking links that seem suspicious or avoid downloading files from unapproved sources.
Phishing
Phishing is one kind of social engineering that aims to help an attacker obtain passwords, credit card numbers, and other personal data. The cyberthreat could be a pop up window saying something like free and easy money, an email, a message saying call the bank, any message saying that is from the banks or any official authority. In order to avoid phishing pointers, it is also important to avoid providing links or files from unknown sources. This is why one should make sure they select a robust password while protecting the account through two-factor authentication.
Distributed Denial of Services
One type of cyber oppression is called DDoS (Distributed Denial of Services) attack, where a network or website inundates with traffic and creates an impediment to access by legal users. One of the tools included in the attacker’s arsenal is botnet attacks that involve the establishment of control over computer networks. If you want to mitigate DDoS attacks you have to use a DDoS protection service, monitor input and output traffic and, most importantly, have a contingency plan for when everything goes wrong.
Insider Threats
The type of cyber threats that originate from within a firm are called insider threats. Whether acted with premeditation or not, the performers can negatively affect the financial report of the company and its image. It is a hazard since it involves partners or employees with a possibility of accessing personal details of individuals. To avoid insider threats, you should really focus on making security awareness training as a routine exercise, observe human behavior, and strictly regulate access.
MITM
This can be achieved by use of Man-in the Middle (MITM), which is an intrusion technique prevailing in computer networks and telecommunications that allow an attacker to eavesdrop on, intercept, and even influence the communication sessions between two parties. Apart from impersonating the user and gaining his/her identification data, the hacker may also alter the data and track conversations. To avoid using open Wi-Fi connections, it is recommended to apply secure connection like SLS/TLS to defend oneself from MITM attacks.
In this world of technological advancements, the threat of having data stolen by a cyber-threat could happen to any company. It is important that you act to protect your assets appropriately in this era. When it comes to possible cyber risks, and implementing these preventive measures you could decrease your likelihood of a cyber attack and protect your business.
Identify System Vulnerabilities
To many, identifying the points of weakness that the hackers will use to bring down your system is one of the most crucial steps in system security. Yet another important component of cyber security is called vulnerability assessment; this is an identification of the points of access to the system that can be potentially penetrated by an attacker. It requires scanning all the system components of the hardware as well as the software in an attempt to find out the weaknesses. And in this section, we will discuss how one can search for system vulnerability so that you can protect your property.
Perform a Vulnerability Analysis
One of the ways of identifying security loopholes in any system is through performing vulnerability scans. The vulnerability scan procedure involves searching for specific weaknesses in systems with the help of various programs. This is done at a software level and the program will tell one where it think is most at risk and with what level of risk.
Verify any penetrations
It means introducing an assault on your system to experience it firsthand In other words penetration testing means. From the above information it’s clear that penetration testing is more efficient than vulnerability scanning in terms of identifying flaws.
Verify Your Configurations
Actually, the configuration is often viewed as the most common cause of system openings. It is important to check that all your system settings are properly configured in the right level for the highest security measures. Here are the network configurations, users and system authorities, configured firewalls and network barriers.
Monitor your System
Some of the benefits that you are bound to derive from the implementation of monitoring include; Monitoring your system will enable you to note any activity that goes astray and that could be as a result of a vulnerability. In this case, every single traffic in the network, and the actions performed by users are recorded as logs. There might be limitations to theuseer access, monitoring systems, and other security measures.
If you don’t want to lose the resources of your business, you need to find out any regularity gaps. Just like an information security analyst, proper management is crucial for maintaining the safety and security of our system.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity
Securing computer systems, networking devices, servers, and hardware equipment is crucial to safeguarding information and data from unauthorized access.. As the number of cyber threats continues to grow day by day with increased complexity, it is crucial to follow some fundamental strategies that work.
Make a Secure Password
Implementing proper passwords enhancement also helps in the enhanced cybersecurity. Some common practices of creating passwords are as follows: passwords should contain letters in both upper and lower cases, numbers, and/or special characters. The password should not contain or suggest any identifiable information such as name, address, or date of birth. It can be such a headache; people do not repeat the same password when creating accounts with different platforms. To avoid hackers penetrating your details, it is advisable to change passwords frequently
Regularly Update Your Software
To correct these problem and vulnerabilities, Sometimes software has to be updated. It is critical to always update all the software to protect against such weaknesses despite the requirements to update security software only. Often it is necessary to ensure that the newest version of the software is installed, and this may be done if you allow the corresponding option of the automatic software updates.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication
Another feature is the use of several factors in the identification process, so-called multi-factor authentication. Two factors of identity have to input during the login process for instance a password plus a token that is sent to a mobile device. A strong means of protecting your information from unauthorized accounts is through utilization of multi-factor authentication.
Set Up Antivirus Software
Antivirus software comes as a handy tool that helps one to recognize and delete config applications that are not effective and could be hazardous on a computer. A computer user should constantly update their AV software to protect their valuables from virus, malware, and other shad’ software.
Frequently Backup Your Data
For the data which can be regained in case of any risk from the cybercriminals or system mishap, making copies of the data is crucial. Data should be copied by the user to external hard drive or to a remote server through the internet. Ensure that you take a backup to ensure that the data could be retrieved in cases of cyber intrusion or data corruption.
Implement Firewalls
A Firewall is one of the most effective defense mechanisms that can ensure your network has protection against hackers. The operating system is also another significant component of the computer since it mediates between the computers and the internet. Firewalls restrict inbound traffic which is not desirable thanks to the approval of traffic only in your network only. Firewalls come in two varieties to safeguard your data: What is clear is that TV needs hardware and software. There are two forms of firewalls, the first category involves software and these can be installed directly into the computer while the second form of firewalls are in-built in routers and this are referred to as hardware firewalls.
Data Encryption
Encryption means to check a code to protect data from attacks such as hacking by unauthorized persons. The personal data and information regarding finance and trade both belonging to the client and Trend Micro as well as other forms of company asset are protected through encryption. There are several techniques present these are hashing and symmetric as well as asymmetric techniques. When it comes to the encryption tools that can be used to protect the information, there are popular products, including Bitlocker, 7-zip, and Veracrypt.
Virtual Private Network
Perhaps the most effective cybersecurity solutions for maintaining your anonymity and protecting your digital identity are VPN. To ensure that hackers do not monitor your movements online, this can mask the transmission of internet traffic and camouflage your IP address. As it stands, the internet contains many free and paid VPN services, and the number is growing more and more. There are providers such as Cyberghost, ExpressVPN, and NordVPN among others.
A cyber attack happens when hackers try to invade an organization’s computer systems without authorization to create maximum chaos. Regrettably, every organization is vulnerable to cyber attacks because it is simple for individuals to impersonate others online. This makes it important that every organization establishes measures that allows it to quickly respond to a cyber attack.
Once a cyber attack is observed, one must not delay, but take the necessary actions against his/her possession to reduce the level of risk. The following steps must be taken in the case of a cyberattack.
figuring out what kind of attack it is
The first step is to figure out what kind of strike it is. You can deal with it by looking for signs of an attack on your system, like slow network speeds and other things. You need to keep an eye out for anything that seems fishy, like illegal access and logins. As soon as you see that your assets are being attacked, you need to take steps to protect them.
Stopping an attack
As soon as you know what kind of attack it is, you need to act quickly to protect your assets from more damage. Systems that are affected might need to be shut down and networks might need to be removed. You should always change your password and other entry information so that someone else can’t get to your data. As a business owner, you should still tell your clients about the attacks and take steps to keep their info safe.
Get Your Data Back
Once the attack is over, the next step is to get the info back. One way to fix this is to reinstall the app and make a copy of the data. You should also keep the software and protection system up to date to stop attacks even more.
Cyberattacks can be dealt with in a number of ways, including:
Rent a protection company from a third party
Getting in touch with police
Make an incident statement
There are pros and cons to each of these choices. You should look over how you handle hacks to protect your assets from more damage.
Keeping your business safe online
These days, businesses focus more on digital tools. So, cybersecurity is important for keeping business resources safe. Cybersecurity is the process of keeping private data and a company’s good name safe. Businesses should care about safety for these reasons, and here are some ways to do it.
The data leak could do a lot of damage to the company’s image. People might stop trusting the business, which would be a terrible waste of time and money. Because of this, security problems can lead to bad press and more damage to a company’s name. So, to keep info safe from hackers, follow the best practices for cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity is a way for businesses to protect their valuables from being hacked. Lastly, make sure you follow the above cybersecurity steps to keep your info safe and ensure long-term success.
Last Thoughts
Businesses should put cybersecurity at the top of their list of priorities to keep their important online assets safe. Even though online threats change all the time, new holes will appear. To stop data breaches and deal with them when they happen, you need a good protection plan. Put up firewalls and antivirus software to protect yourself from hacking, and show your employees how to do the same.
Cyberattacks are less likely to happen if you keep your software up to date and get back any data you may have lost. Companies that want to protect their customers, business, and financial information should think about the above strategies and suggestions. Lastly, make sure that all business deals, no matter how big or small, have a strong foundation.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology
Top Monetization Websites

Top Monetization Websites
Monetization websites have gained significant popularity in recent years as digital entrepreneurs and content creators seek avenues to generate revenue online. In this digital era, people always look for making money from digital platforms. Monetization websites are becoming more popular day by day. However, this platform helps individuals to earn money from their content, skills, and online activities. This article will cover over 30 monetization websites. These platforms offer various methods for individuals and businesses to monetize their content, skills, and online presence. In this article, we will explore the top 100+ monetization websites and provide detailed information about each platform, outlining their key features, monetization methods, and suitability for different types of users.
Google Adsense Monetization

- Google AdSense: Google AdSense is a program run by Google where the website owners and bloggers are offered to display ads on their websites. When the viewers click on view these ads,the individuals can earn money. AdSense works well for all types of content creators. AdSense is easy to use. It also has many options for customization.These advertisements are administered, sorted, and maintained by Google.This program also operates on HTTP cookies. Google uses its technology to serve advertisements based on website content, the user’s geographical location, and other factors.
- Ezoic: Ezoic is a digital platform which helps you place ads on your website in best spots to get maximum earnings. It is also an award-winning technology partner for digital publishers and content creators. This platform leverages artificial intelligence to comprehensively analyze the behaviors of both web visitors and advertisers. However, It tries out different layouts and setups, giving you useful insights to help you make more money. Ezoic is built for everyone, that is ,from bloggers to major brands. It is the first platform built to provide the value of large teams and modern data science without any of the overhead or complexity associated with managing these sophisticated systems. Ezoic was also the recipient of the Google Business Innovation Award.
- Media.net : Media.net is a top advertising network that shows targeted ads. They offer high-quality ads as well as competitive revenue sharing, making it a well built alternative to AdSense. Media.net also has the industry’s first server-side header bidding platform that maximizes yield without compromising the user experience. Their offerings incorporate proprietary machine learning technology, sophisticated data processing, and detailed analytics capabilities to successfully target internet users. By revenue, Media.net is the second-largest contextual advertising business worldwide.
- Infolinks: It is an in-text advertising platform. It converts selected keywords within your content into ad links. Since it has various ad formats, Infolinks is famous among thousands of publishers. Advertisers use Infolinks’ intent-driven ads to reach the right audience and deliver ads in real-time when users are most engaged and relevant. The secret to the success of Infolinks’ advanced ad solutions is the relevance, targeting and unprecedented viewability rates of 90%. They work with thousands of advertisers such as Nike, Virgin Airlines, Target, and Netflix to deliver nearly 1.5 billion monthly ad views.
- PropellerAds: PropellerAds comes up with a variety of ad formats. Pop-under, push notifications and native ads are some of them. PropellerAds assists the Publishers to monetize their websites, mobile apps, or their browser extensions. They provide access to unique traffic sources and Al-based ad-serving / optimization tools for media buyers, agencies, brand owners, and affiliate marketers.
- This includes advanced Demographic and Interests Targeting to find matching audiences, CPA Goal pricing model for automatic bidding and optimization, efficient ad formats (Push, In-Page Push, Interstitial, Popunder) with unique templates for customization,
- Revcontent: Revcontent is a leading content marketing and native advertising platform that leverages lightweight, customizable technology to empower the web’s leading publishers and marketers to reach and exceed their revenue, engagement and growth goals. Revcontent is also native advertising platform. It focusses on delivering high-quality content recommendations to engage users. Revcontent’s personalized ad widgets deliver a smooth interaction with your website while monetizing your audience.
- Taboola: Taboola is a top content discovery and native advertising platform which can provide personalized content to publishers recommendations to their readers which makes it capable of monetization strategy. The company’s platform, powered by artificial intelligence, is used by digital properties, including websites, devices and mobile apps, to drive monetization and user engagement. Taboola has long-term partnerships with some of the top digital properties in the world, including CNBC, NBC News, Business Insider, The Independent and El Mundo.
- Adversal: Adversal, which is a CPM-based advertising network, provides competitive pricing to the publishers. They have various ad formats and advanced targeting options and hence are a great choice for monetizing one’s website.
- Sovrn //Commerce: Sovrn //Commerce previously known as VigLink is a perfect affiliate marketing platform. It serves the purpose of automatically converting product links into the so-called affiliate links. When individuals use these links, publishers earn a commission.Sovrn Commerce empowers publishers and content creators to effortlessly generate income through monetized affiliate links. With their user-friendly extension, you can seamlessly convert any product page into a shareable link, allowing one to earn commissions from clicks or sales resulting from that link.
- Skimlinks: Skimlinks is an affiliate marketing platform. They help publishers to monetize their content. It is done through affiliate links. It can also automatically convert product mentions into affiliate links which allows the publishers to earn commissions from relevant purchases. Skimlinks powers commerce content strategies for publishers. They are the world’s largest commerce content monetisation platform, it helps grow a revenue stream that can contribute as much as a quarter of a publisher’s overall revenue, which enables publishers to be less dependent on advertising. Its technology automatically earns publishers a share of sales they drive through product links in commerce-related content created by editors. The platform is a one stop solution providing the technology and the data to start, grow and successfully scale a content commerce strategy across desktop, tablet and mobile.
- Adsterra: Adsterra, known for its broad range of advertising network, offers various ad formats including pop-ups, banners, push notifications, along with interstitial advertisements. They have a 3-level security system, many flexible ad inventories, and industry’s best managers and support. Comprehensive targeting options are also available. Adsterra has been a choice for publishers because of its competitive pricing. Malware is strictly prohibited, along with redirects, unsolicited downloads, and virus alerts.
- Bidvertiser: Bidvertiser is an advertising network. Their main Focus is on technology, optimization and automation. It permits the publishers to display text advertisements, banner ads, native ads, and programmatic XML on their websites. They are also efficient in Real-time bidding and optimization. These features help to maximize the revenue of the same. Bidvertiser operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers bid for placement in publisher websites’ ad slots. This dynamic auction-based system ensures that ads are displayed to the most relevant audience, maximizing both advertisers’ ROI and publishers’ earnings.
- Revive Adserver: Revive Adserver is a free open-source ad serving system that allows the publishers to serve ads on their websites. They have advanced targeting options and tracking capabilities. Also, they offer flexibility for revenue generation. They even define rules for delivery of campaigns and ads, including frequency capping, URL targeting, geo-targeting. And then Track campaign performance, including impressions, clicks, click-through rates, conversion rates, revenue, eCPM, and conversion details, like basket value and number of items purchased.
- AdRecover: AdRecover permits the publishers to regain revenue from ad-block users. This is done by displaying non-intrusive ads. AdRecover gives backup revenue stream while maintaining a positive user experience. AdRecover is a user-friendly solution to recover lost revenue due to adblocked traffic. AdRecover never compromises the user experience, creating a win-win situation for the visitors as well as the publishers. AdRecover educates the users about how banner ads help keep the world’s information free, accessible and the editorial unbiased. Users have an option to opt-out and report when they don’t like certain ads, on which we ensure prompt action.
- BuySellAds: This usually is a marketplace connecting publishers and advertisers. BuySellAds helps publishers to sell ad space directly to interested advertisers. They also render control over pricing and deals.Their tools, and services help marketers easily reach their target audience with contextual advertising, and publishers monetize their websites, newsletters, and podcasts. Specializes in cross-channel advertising, self-serve advertising, native advertising, sponsored content, email advertising, podcast advertising, display advertising, newsletter sponsorships.
- Adbuff: Adbuff is an ad network that focuses on high-quality ads. They are primarily centered on premium publishers. Adbuff is a platform for monetization having competitive CPM rates and real-time bidding. They help brands maximize their marketing ROI and make them more Memorable, Impactful and Profitable. They specialize in Facebook Ads, Instagram Ads, E-commerce Strategy, Google Ads, Amazon Ads, Performance Creatives, Shopify, Shopify App.
- AdMaven: AdMaven is mastered in pop-unders, push notifications, and also interstitial ads. They have high CPM rates, advanced targeting options, and a user-friendly interface. Hence, it is popular among the publishers. AdMaven is constantly building an engine which yields an increased revenue for publishers, while enabling advertisers to get high performance and vast distribution for their ad budgets.
- Adcash: Adcash which is a global online advertising platform, offering various ad formats like native ads, push notifications, and interstitial ads. They also have advanced targeting, real-time reporting. And its competitive CPM rates make it a decent choice for publishers. Ad inventories are uniquely optimized and placed according to the campaign’s targeting as well as the website’s individual ad compliance requirements, and vice versa. Maximum exposure is obtained on a wide variety of sites for advertisers to broadcast their offers to the widest possible audience.
- Advertise.com: Advertise.com is an online advertising platform. They also have various ad formats, including display ads, pop-ups, and native ads. It helps publishers with competitive rates and also advanced targeting options. They provide advertisers with high-quality exclusive traffic that performs and yields high ROI. Using our patented Click Shield click scoring technology, Advertise.com guarantees high-quality traffic. And also provide advertisers with quality traffic that converts, and publishers with competitive listings that yield high revenues. Using our patented Click Shield fraud protection software, Advertise.com guarantees high-quality traffic for both advertisers and publishers.
- Adverticum: Adverticum is an ad network which focuses on Central and Eastern European markets and offers various ad formats along with targeting options for publishers in those regions. The development of Adverticum AdServer works out by harmonizing global market trends and local client needs. Adverticum is engaged in providing great product support and in fulfilling unique needs of its clients flexibly.
- Adverty: Adverty is an in-game advertising platform. Also enables publishers to monetize their games. It includes non-intrusive ad placements that offer immersive and interactive ad experiences. It enables new gaming revenue streams for developers and empowers advertisers to reach uniquely engaged audiences. Adverty delivers spectacular In-Play ads to connect brands and people through its revolutionary and multi-patented technology built for VR/AR and mobile games. The platform offers programmatic video and display ad inventory at scale and allows content creators to monetise the complete experience with unobtrusive, easy-to-integrate, immersive ads.
- Adzerk: Adzerk is an ad serving platform that allows publishers to manage and optimize their ad inventory. It provides advanced targeting options and real-time reporting. Adzerk is “ad serving as an API”, a collection of products that enable developers to build native ads and integrate advertising into their properties.
- Adstargets: Adstargets is a self-serve advertising platform offering various ad formats, including native ads, pop-ups, and banners. Advanced targeting options and real-time analytics help optimize monetization.
- Affiliate Window: Affiliate Window as the name suggests, is an affiliate marketing network that binds the advertisers and publishers. It provides a variety of affiliate programs. And also helps publishers with advanced tracking and reporting features. Affiliate Window is a global performance marketing network with an innovative and ethical approach to performance marketing.
- Adkernel: Adkernel is an ad serving platform. It offers real-time bidding and optimization features for systematic monetization. Adkernel helps publishers with advanced ad management capabilities. They offer Programmatic Display & Video White-label Ad Serving Solution, Programmatic White-label Media-buying Platform (DSP), Server Side Header Bidding platform (prebid compatible), Variety optimization and analytic tools. The company’s industry-leading role provides enterprise-class solutions for pay-per-click, display and video, mobile and desktop markets.
- AdMantX: AdMantX which is an AI-powered advertising platform that provides advanced targeting and ad verification capabilities to publishers. It presents high-quality ads and personalized support. They specialize in Semantic Targeting, Contextual Advertising, Semantic Technology, Natural Language Processing, Audience Targeting, Artificial Intelligence, Advanced Profiling Services. ADmantX provides contextual analysis and data, offering a cookie-less solution for publishers and advertisers to develop online advertising.
- Adperio: Adperio is a performance-based advertising network that concentrates on mobile app monetization. Their platform provides various ad formats and targeting options for publishers. This leads to maximizing their revenue potential. Adperio, who is now Perform[cb], offers strategic plans tailored to meet their clients’ specific marketing goals. Perform[cb] is the pioneer of performance marketing and uniquely positioned to lead this space based on brand trust, team experience, compliance best practices and technological innovation.
- AdPushup: This is a revenue optimization platform that empowers the publishers to increase their ad revenue. This is done by automating A/B testing. It also has strategic ad layout optimization. They help web publishers grow their advertising revenue by using cutting-edge technology, premium demand partnerships.
- AdRiver: AdRiver is an ad serving platform. They provide advanced targeting options. It is the real-time reporting that enables publishers to manage and deliver ads on their websites. They are also leading Mobile Out of Home providers in Europe. AdRiver brings exclusive tech solutions to brands to guarantee them transparency and efficiency in their campaigns.
- Adstir: Adstir is a mobile advertising platform that has a wide range of ad formats, including banner ads, interstitial ads, and also rewarded videos. Adstir helps publishers with powerful targeting options and real-time analytics.Through their PMP marketplace, they deliver high-priced and premium ads. They do CPM evaluation and optimization from a fair perspective on the basis of the number of impressions counted by Ad network.
- AdSupply: AdSupply is a digital marketing company that focuses on delivering visible CPM advertising. They offer innovative ad formats and targeting options for publishers looking to monetize their audience. AdSupply creates patented, world-class ad tech that delivers viewable, high impact ad formats for brands, agencies and publishers looking to maximize Return of investment. They automatically redirect traffic in case they detect that there are no available ads from the ad network to another network.
- Adtelligent: Adtelligent is an advertising technology company that helps publishers with advanced ad serving. They also provide monetization solutions to publishers. It offers various ad formats and optimization features. They also specialize in Video Advertising, VAST/VPAID Compliant Player, Video Ad Marketplace, Header Bidding Wrapper Programmatic Buying, Ad Serving. Display Advertising, Native Advertising, Header Bidding, Banner Advertising.
- Adthink: Adthink, an advertising network, provides varieties of advertising formats, encompassing display ads, pop-unders, and also native ads. They help publishers with competitive rates and targeting options. They also cater to a spectrum of promotional needs to customers. Adthink addresses the B2C market by developing a global digital and physical distribution platform and the B2B market by providing advertisers with its trading desk and affiliate platform to develop their customer acquisition. With its proprietary adtech solution AdAccess, media publishers can optimize and multiply their revenue channels.
- AdTiming: AdTiming known as a global mobile advertising platform, offering a wide range of ad types, such as interstitial ads, rewarded videos, and native ads. It empowers publishers with real-time information and advanced targeting choices that can lead to the enhancement of their advertising strategy.They cater to e-commerce, games, utilities and social applications. It is a comprehensive supply chain from advertisement to monetization.
- AdTradr: AdTradr which is known for its programmatic advertising, bridges the gap between publishers and advertisers. And also advanced targeting choices. Its aim is to make the digital advertising space a healthier and more efficient landscape. Alternatives and possible competitors to AdTrader include Amura Marketing Technologies and Embold.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

The Ever-Expanding Frontier: Securing the Wild West of the IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as an evolutionary force, reforming industries and everyday life in the digital era. With this technical breakthrough comes a new frontier, similar to the Wild West, where security concerns are paramount. While the businesses undertake digital transformation plans, the need to secure the expanding realm of IoT devices becomes the prime factor. The internet of things, or IoT, is a network of interrelated devices that connect and exchange data with other IoT devices and the cloud. IoT devices are typically embedded with technology such as sensors and software and can include mechanical and digital machines and consumer objects.
Increasingly, organizations in a variety of industries are using IoT to operate more efficiently, deliver enhanced customer service, improve decision-making and increase the value of the business. With IoT, data is transferable over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interactions. Computer Engineers have been adding sensors and processors to everyday objects since the 90s. However, progress was initially slow because the chips were big and bulky. Low power computer chips called RFID tags were first used to track expensive equipment. As computing devices shrank in size, these chips also became smaller, faster, and smarter over time.
Thanks to the advent of inexpensive computer chips and high bandwidth telecommunication, we now have billions of devices connected to the internet. This means everyday devices like toothbrushes, vacuums, cars, and machines can use sensors to collect data and respond intelligently to users. This article is about the challenges as well as strategies for securing the Wild West of the Internet of Things.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Rise of IoT in Digital Transformation Strategies:
Digital transformation strategies have become recalibrated for businesses to stay in today’s competing dynamic market. At the heart of this transformation lies IoT, a network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data. From smart homes and wearable devices to industrial machinery and smart cities, IoT applications are diverse and far-reaching. Despite being a critical element in digital transformation, IoT is often overlooked when businesses are laying out their strategies for digital innovation. However, the fast spread of IoT devices has overtaken the development of security measures, leaving them vulnerable to cyber assaults.
As more devices become interconnected, leading to the expansion of the attack surface, it exposes critical infrastructure and sensitive data to potential compromise.IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway, which acts as a central hub where IoT devices can send data. Before the data is shared, it can also be sent to an edge device where that data is analyzed locally. Analyzing data locally reduces the volume of data sent to the cloud, which minimizes bandwidth consumption.
Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they get from one another. The devices do most of the work without human intervention, although people can interact with the devices — for example, to set them up, give them instructions or access the data. The connectivity, networking and communication protocols used with these web-enabled devices largely depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
Challenges on the Digital Frontier are:
The challenges include: Increase in the attack surface as the number of connected devices grows. As more information is shared between devices, the potential for a hacker to steal confidential information increases. Also Makes device management challenging as the number of IoT devices increases. Organizations might eventually have to deal with a massive number of IoT devices, and collecting and managing the data from all those devices could be challenging. It Has the potential to corrupt other connected devices if there’s a bug in the system. TheyIncreases compatibility issues between devices, as there’s no international standard of compatibility for IoT. This makes it difficult for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other. The others are as follows:
Weak Authentication and Passwords: Many IoT devices ship with flimsy, pre-set credentials or simple password protection. A great example of this is the equivalent of leaving your saloon door wide open with a welcome sign for any digital outlaw. Hackers can easily exploit these vulnerabilities to gain control of devices and launch attacks on connected networks.
Data Privacy Concerns: IoT devices often collect vast amounts of personal data, from our daily routines. Many IoT devices are vulnerable to hackers and other cyberthreats, which can compromise the security and privacy of sensitive data. IoT devices can also collect vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data protection. Even our intimate health information. This data, if not protected, becomes a goldmine for venomous actors, leading to identity theft, targeted advertising, and can even lead to blackmailing.
Lack of Standardization: The diverse landscape of IoT devices, with abundant manufacturers and protocols, hinders a unified approach to security systems. Imagine horses, carriages, and spaceships trying to navigate the same dusty trail – there’s bound to be a collision if everyone follows their own rules by themselves.
Outdated Firmware and Patch Management: Many IoT devices have infrequent or nonexistent firmware updates, leaving them vulnerable to known exploits. It’s like riding a stagecoach riddled with bullet holes, hoping it won’t fall apart on the next bandit ambush. Outdated or insecurely built software creates gaps in this fence, making it easier for attackers to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive data, like credit card information. Patch management helps to strengthen this fence, ensuring its integrity and reducing the risk of a data breach.
Physical Tampering and Inaccessibility: Some IoT devices lack basic physical security measures, making them susceptible to tampering. Imagine a saloon safe built of cardboard – any determined varmint could break in and steal the loot.The security of IoT infrastructure should not be the exclusive responsibility of the cyber security team. Establish cooperation and shared responsibility between the cyber security team, operations and management team, and physical security team. Getting all three involved will ensure the best outcome.Remove any connectivity hardware—optical ports, radios—that exist purely for development reasons.
Also, if it makes sense given the structure and purpose of the devices, consider removing all test points or disabling test access and otherwise secure devices from unauthorized digital access. Any sort of test or admin access is likely to be the target used by attackers. Ensure all devices are in operations mode and not accidentally left in default setup, reset or pairing modes. Additionally, embedded systems within critical infrastructure might be inaccessible for traditional security solutions.
Building a Secure Frontier Town:
Just like the Wild West eventually found its law and order, Here are some key approaches to mitigate IoT security risks :
Strong Authentication and Encryption:It is widely known that users often do not take the extra step of changing the default username and password of their IoT device, thus leaving it completely vulnerable to password-guessing and cracking attacks like credential stuffing, brute-forcing, dictionary-based guessing, masked or rule-based guessing, and even using the help of trained neural networks to generate thousands of highly plausible guesses. Implementing multi-factor authentication and robust encryption protocols (like WPA3) strengthens the gates of the digital town, making it harder for outlaws to break through.
Data Minimization and Privacy Controls: Implementing the principle of “least privilege” which says that Principle in computer security that every module must be able to access only the information and resources that are necessary for its legitimate purpose and giving users granular control over data collection and usage empowers them to protect their digital nuggets.
Standardization and Open Platforms: Promoting industry-wide standards and open platforms fosters collaboration and creates a shared set of security rules, akin to a town sheriff uniting different factions.
Secure Firmware Updates and Patch Management: Patch management is the process of applying updates to software, drivers, and firmware to protect against vulnerabilities. Effective patch management also helps ensure the best operating performance of systems, boosting productivity. Establishing a system for regular and automatic firmware updates ensures the townsfolk are always armed with the latest defensive measures against evolving threats.
Physical Security and Remote Management: Proper (sufficient) security controls must be implemented at the web, software application, and OS or firmware level to ensure the best possible protection of security and privacy at each layer of an IoT device, but given the fact that these devices are often characterized by their restricted memory capacity, low energy, and limited processing power, it is often quite challenging to properly implement sufficient security measures in IoT devices as their hardware and subsequent software limitations pose a huge barrier for software developers while implementing core functionalities of the device.
Implementing tamper-proof hardware and remote access controls, akin to a fortified bank vault, makes it harder for physical attacks and easier to monitor and manage security remotely.
Beyond the Lone Ranger:
Securing the IoT frontier requires a collaborative and collective effort. Manufacturers need to prioritize security by design, consumers should be attentive about choosing secure devices and practicing safe usage habits, and also governments must play a role in fostering regulatory frameworks and promoting best practices. All these mentioned above should go hand in hand. By working together, we can transform the Wild West of the IoT into a thriving, secure community, where innovation multiplies with peace of mind. Remember, in the digital frontier, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure – let’s build a future where connected devices empower us, not put us in danger.
Implement Robust Authentication and Encryption:
Strong authentication mechanisms play a crucial role in preventing unauthorized access to IoT devices. Multi-factor authentication, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, adds an extra layer of security beyond traditional passwords and systems. Additionally, certificate-based authentication leverages cryptographic certificates to check the identity of devices and users, ensuring only trusted entities can access sensitive data or control IoT devices.
And hence, encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS should be employed to safeguard data both in transit and at rest. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols ( Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security protocol that provides privacy, authentication, and integrity to Internet communications. SSL eventually evolved into Transport Layer Security (TLS) ) encrypt data communications between IoT devices and servers, preventing eavesdropping and data tampering by malicious actors. By implementing robust authentication and encryption measures, organizations can significantly enhance the security posture of their IoT deployments.
Regular Security Updates and Patch Management:
Manufacturers should prioritize regular security updates and patch management to address known vulnerabilities and mitigate emerging threats in Iot. Software vulnerabilities are frequently discovered in IoT devices, exposing them to potential exploitation by cybercriminals. Automated update mechanisms streamline the process of deploying patches, ensuring timely protection against newly identified security flaws. By promptly addressing vulnerabilities through regular updates, manufacturers can reduce the risk of IoT devices being compromised and prevent them from becoming entry points for cyber attacks.
Effective patch management is essential to maintaining the security and integrity of IoT ecosystems, safeguarding both user data and critical infrastructure. Also Effective patch management is a systematic and repeatable patch distribution process for closing IT system vulnerabilities in an enterprise. It involves pervasive system updates, including any or all the following: drivers, operating systems, scripts, applications, or data files.
Network Segmentation and Access Control:
Segmenting IoT devices into distinct network zones based on their function and security requirements is essential for minimizing the impact of potential breaches. By partitioning the network into separate segments, organizations can contain security incidents and prevent lateral movement by cyber attackers. Implementing access control policies based on the principle of least privilege ensures that only authorized users and devices have access to specific resources and functionalities. By restricting access to IoT devices and services based on predefined rules, organizations can reduce the attack surface and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
Network segmentation and access control measures are critical components of a comprehensive IoT security strategy, enabling organizations to proactively defend against cyber threats. Network micro-segmentation enables isolation of less-capable devices at the network layer, either behind a gateway or on a discrete network segment. Network segmentation leverages an EVPN-VXLAN architecture that supports a highly scalable and agile environment while maintaining the security and performance requirements needed to protect users and IoT devices.
Privacy by Design:
Privacy should be integrated into the design and development of IoT solutions from the outset to protect user data and build trust with consumers. Privacy-enhancing technologies such as anonymization and data minimization help mitigate privacy risks associated with IoT deployments. Anonymization techniques strip personally identifiable information from data collected by IoT devices, preserving user anonymity and confidentiality. Data minimization (Data minimisation means collecting the minimum amount of personal data that you need to deliver an individual element of your service.
It means you cannot collect more data than you need to provide the elements of a service the child actually wants to use) practices limit the collection and retention of sensitive information to the minimum necessary for the intended purpose, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and misuse. By adopting privacy by design principles, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to protecting user privacy and comply with regulatory requirements governing data protection.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection:
Implementing real-time monitoring solutions and anomaly detection algorithms is essential for detecting suspicious behavior and potential security incidents in IoT environments. Continuous monitoring of network traffic, device activity, and system logs allows organizations to identify anomalies indicative of unauthorized access or malicious activity. Anomaly detection algorithms analyze patterns and deviations from normal behavior, alerting security teams to potential security threats in real-time. Rapid incident response mechanisms should be in place to contain and mitigate the impact of security breaches, minimizing downtime and data loss.
By maintaining continuous vigilance and proactive threat detection capabilities, organizations can effectively defend against evolving cyber threats and protect their IoT infrastructure from exploitation. By implementing these comprehensive strategies, businesses can significantly enhance the security of their IoT systems. This proactive approach helps to mitigate the inherent risks associated with the rapidly growing landscape of the Internet of Things. By doing so, companies can protect their valuable data and maintain the integrity of their connected devices, ensuring a safer and more resilient technological environment.
Conclusion:
Securing the Wild West of the Internet of Things is a complex and ongoing challenge that requires concerted efforts from industry stakeholders, policymakers, and cybersecurity professionals. By adopting proactive security measures and adhering to best practices, businesses can navigate the IoT landscape safely and reap the benefits of digital transformation without compromising security and privacy. As the frontier of IoT continues to expand, vigilance and innovation will be key to taming the Wild West of the digital age.IoT devices are increasingly being used by individuals and across the enterprise. They are not only here to stay, but proliferating exponentially in more and more forms. The result is increasing complexity, which hampers efforts to manage IoT systems security successfully.
IoT security challenges range from deflecting malicious insiders to defending against nation-state attacks. Because of the inherent vulnerability of IoT devices and the scale of their deployment, attacks continue to grow in scale and scope. Securing IoT devices is well worth the investment despite the IoT security challenges. The value realized with IoT devices can only be increased with enhanced security to be on par with other technology. It will mitigate risks and increase the rewards.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

Cloud Computing Security Best Practices and Considerations: Safeguarding Your Digital Assets
Cloud Computing Security Best Practices: An individual is supposed to protect his/her digital assets in the same way as physical ones are protected.
Introduction:
Cloud computing presents many opportunities for corporations in terms of the scale, cost, and accessibility of computer resources. However, due to the heavy dependence on cloud services, how they protect data is an issue that deserves utmost attention. To avoid compromise of data and applications in the cloud, organizations have to use at least proper practices as well as consider several factors. To get you up to speed with cloud computing security measures, this extensive article covers the key guide on cloud computing security to enable businesses to reduce risks and ensure data confidentiality, integrity, as well as availability.

Data Encryption:
The Importance of Encryption
We start with protection of data through encryption as an integral preventive mechanism against threats in cloud environments. It is the process through which information is transformed to a mode that cannot be understood without a decryption tool. This makes certain that even when the data is intercepted or retrieved from the system by malicious users, they cannot comprehend or retrieve the data.
Best Practices for Data Encryption
Furthermore, data has been receiving more attention recently, which is understandable given its significance for all types of organizations and businesses, from startups to established ones. Utilizing data encryption technologies is one method of protecting data. Although there are many ways to secure data, the following guidelines suggest encrypting data:
Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit: To prevent unwanted access, data must be continuously encrypted while it is stored on the cloud (also called “data at rest”) and while it travels between locations (sometimes called “data in transit”).This helps to avoid infringement during both storage and transmission of interfaced data communications.
Use Strong Encryption Algorithms: Ensure that data is encrypted using a combination of advanced algorithms such as the Advanced Encryption Standard-256 for data in storage, and Transport Layer Security 1. Data in transit, in contrast, could generally be kept at 2 or higher. These standards are also popular in their security measure.
Secure Key Management: Maintaining security and privacy of keys and Key management is another pivotal issue as vital as encryption. Hardware security modules (HSM) are designed to hold the encryption keys while cloud key management services (KMS) offer the process as a service. Additional measures that can be observed is that key rotation polices actually add layers to security.
End-to-End Encryption: Protect the data by designing mechanisms that encipher the data at the stage of creation and afterwards during storage and disposal. This includes data backup or storing data in archives.
Identity management solutions in cloud computing
Identity and Access Management or Identity and Access Control or simply IAM is one of the key aspects that are relevant while considering the cloud security. This involves access mechanisms, such as identities of the user and resources and tools that are used to authenticate the same. The way IAM is done ensures that any individual that tries to access data or any application that is reserved for certain users only is locked out.
Best Practices for IAM
Implement Strong Password Policies: The qualitative studies were also based on the following measures: Conduct compliance audits regularly with strict password legislation to ensure that users choose difficult passwords and change them often. Avoid password sameness and promote passphrase.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Therefore it is recommendable to employ MFA to enhance security by adding another level of barrier to access one’s account. It entails the use of two or more verification factors to be used when preparing to access the platform to minimize incidences of a breach in the credentials.
Network Segmentation: Segment the network into smaller subnets that are not interconnected such as a DMZ or demilitarized space. This approach has the possibility of risks and is really good in securing some valuable assets.
Use intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to periodically check the network for any unusual behavior and stop it before it has a chance to become a serious danger.
Frequent observation of the network: Watch out for unusual activity at all times to possibly uncover security lapses and intrusions: Employ event management and security information to keep an eye on dangers in real time.
Vulnerability Assessments: Carry out periodic security audit to uncover possibly existing security weaknesses. Patch learned his or her mistakes in terms of weaknesses identification so that the he or she did not give a chance to the attacker to take advantage.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
A backup can be defined as the preservation of data and information which takes various forms and is classified depending on the form it takes into several categories as follows;
Ensuring Business Continuity
Business continuity is critical and so is the reliability of cloud-based backup and disaster recovery programs. It is beneficial to periodically copy and store essential data, as well as distribute Copies of such data across different geographical locations or availability zones to minimize data loss and increase the speed of restoring data.
There are several special best practices for data backup and disaster recovery including:
Regular Backups: Back up frequently accessed data and application data to ensure that recent data can be reproduced in case of data loss. There are number automated backup solutions that can help in this process.
Geographic Redundancy: Location backups in different geographical area or in different availability zones will help in handling the regional calamities and for provision of data access.
Testing Restore Processes: Perform some disaster recoveries from time to time, to confirm that backup can be recovered easily. This confirms that the shied data backups are complete and reliable.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO): Set RTOs to identify the actual tolerance time for essential systems and processes outage. It is important that the organizations take the following steps to achieve the set goals in the realization of these objectives.
Recovery Point Objectives (RPO): Define RTOs to identify the maximum timeframe of business disruption to put into practice the acceptable data loss. To achieve this, ensure the back-up you schedule meets the particular Recovery Point Objectives set to reduce data loss.
Security Patch Management
Security patch management is a vital component of any business or organization because the absence of proper security patch management leads to security breaches that affect the business or organization.
Best Practices for Security Patch Management
Automated Patch Management: Automate the process of patch and update management by installing appropriate tools that would help in popping up the patches and updates once released. It also minimizes human intervention hence; there is proper timing in updating the indices.
Vulnerability Scanning Tools: Continue your vulnerability scanning to discover such threats and patch management progression. A few checks in a day are highly essential to ensure that there is no penetrating security threat in the system.
Monitoring Security Advisories: As a user, ensure that you are up to date with the newest security notices from your OS and application developers and cloud solution partners. Seamlessly implement fixes for newly discovered vulnerabilities as it is critical to avoid compromising the system.
Patch Testing: To develop test patches first develop them in a staging environment before going to the actual production site. This makes it easier to ensure compatibility, and thus reduces the potential for interference or disruptions.
Incident Response and Monitoring
Preparing for Security Incidents
Relating to the need of every computer system to have an incident response, it has been established that every system must have the following; Using IDS, upgraded SIEM tools, and log monitoring solutions are the ways through which it is possible to detect threats as they occur in realtime.
This paper contains recommendations that can be followed when dealing with incidents and also the procedures that should be taken in reviewing the incidents.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): On this level it is necessary to deploy IDS to monitor the traffic for any suspicious activity. There is also IDS intrusions which are capable to identify and notify security groups of the potential violations.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Engage with SIEM when it is time to compile and parse as well as correlate security information which has been gotten from different points. SIEM allows for identifying adverse events in real-time and managing them through a single point of contact.
Log Monitoring Solutions: Begin practice of log usage monitoring and implement solutions for logs used in cloud resources. It helps in detecting outliers and suspicious activities of security flaws.
Establish a core team to handle security incidents and give them the authority to look into and address security concerns. This is known as the incident response team. It’s also critical that the right individuals are prepared to address the issue with the necessary training and tools.
Regular Security Drills: Ensure that institutions maintain regular security drills in their quest to enhance response to security threats. It is quite obvious that the flaws of the plan have to be pointed out and strengthened during the simulated exercises.
Evaluating Cloud Service Providers
Specifically, while choosing CSP, one has to pay attention to the security measures and standards that the CSP follows. The next step is to assess how well the provider meets various standards and requirements, for instance, being ISO 27001 certified, accredited with SOC 2, or following the provisions of the GDPR.
Security assessment of a cloud provider: Key issues and approaches
Compliance and Certifications: Thus, it is also important to ensure that the selected cloud provider meets all legal requirements and fulfills industry standards. Search for Service organization control SOC 2 type 2, ISO 27001, and General data protection regulation GDPR.
Security Practices and Policies: Consider security standards of the cloud provider. Make sure that they meet not only your organization’s security needs and standards, practices, and procedures.
Incident Response and Support: Rate the response to security incidents based on the selected cloud provider’s experience and approach. Make sure they have an efficient mechanism for managing security breaches and provide them with assistance in the worst-case scenario.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
There has been a significant concern over data protection and privacy, especially when data is stored and processed on cloud. Learn with legalities that pertain to your chosen trading sector and country or state policies that apply to your trade business.
Data Privacy Controls: Adopt the right measures to protect the privacy of data that is collected in the organization. This includes ensuring that the data gathered is anon, and encrypted in addition to applying access restrictions.
Data Retention Policies: Stipulate when information should be deleted or discarded to prevent the unnecessary storage or accumulation of data. Preserve information in accordance with policy and/or legal standards on recordkeeping and disposal.
Compliance with Regulations: The company must consider particular data protection and privacy laws that can apply to the business in specific situations, for example, GDPR or HIPAA.
Best Practices for Regular Audits and Assessments
Security Risk Assessments: Conduct a risk analysis to determine the level of risk that is being posed by the clouds to the entire security infrastructure. Risk analysis required in order to ensure that security measures are deployed to prevent the leakage of data as well as to ensure the protection of the applications.
Policy and Procedure Reviews: Continuously assess and modify security policies and processes over time according to relevant audits or newly identified threats. You should also ensure that the policies in your organization align with the principles of good practice as well as the legal requirements that it has to meet.
Conclusion
Security in cloud computing environments has to be properly implemented to prevent various unauthorized alterations or attacks. Some of the recommended standards for the optimal cloud security include data encryption, stringent identity and access management among others, network security, and efficient handling of security incidents that may occur within a cloud system. Security should remain a moving target while current techniques and methods should be examined and enhanced in order to counter them in the evolving environment of the cloud.
Other factors that need to be considered for higher level security on the cloud:
Advanced Threat Protection
With an increasing sophistication in computer criminals, it is important to get the best in threat protection mechanisms. Organizations should implement advanced security solutions such as:
Machine Learning and AI: Use a machine learning and artificial intelligence powered system to identify threats and manage them in real-time. Security tools that incorporate the use of AI can analyze certain data and recognize certain trends that a human might not be able to detect.
Behavioral Analytics: Use behavioral analytics incidentally to maintain an eye on the activities of the users with a view of identifying malicious activities. It assists in detecting persons within an organisation who pose a threat or whose accounts have been penetrated by a threat actor.
Zero Trust Security Model: Impose a Zero Trust model of security which levies no trust on the systems whatsoever whether they are on the internal or external network. Wherever the access request is coming from, always approve it but only if you are sure.
Secure Software Development
IT professionals must pay much attention to the security of application developed and deployed in the cloud technologies. Organizations should follow secure software development practices, including:
Secure Coding Standards: Implement good practices for coding that keep hackers at bay and avoid trivial issues like SQL injection and XSS.
Code Reviews and Testing: It is also important to review the code on a periodic basis and penetration test the applications to control for major security issues. Since the testing process is tedious and repetitive, it should be automated using testing tools.
DevSecOps: Use Security as a DevOps practice to make security a concern throughout the SDLC to encourage awareness about security concerns in the software development stages. This new approach, referred to as DevSecOps, has become popular because it involves bringing together development, operations, and security specialists.
Container Security
Containers are popular in clouds due to the detachment capabilities and increasing range of uses. Though these devices present new and fascinating opportunities for users, they also pose new security risks. Best practices for container security include:
Image Scanning: While using images to create containers, ensure that the images do not have any vulnerabilities that can be exploited. Make sure you use base images from reliable sources and always keep those images updated.
Runtime Security: Look for signs of unauthorized activities in container run-time environments, as well as ensure adherence to security procedures. The best way to improve the security of the system is to include runtime protection measures that will enable threats to be detected and acted accordingly.
Least Privilege: Implement SU capability for your containers to run them with the minimum level of access to sensitive data. Do not execute the container in root and organize isolation by using name spaces and groups.
Secure Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Here we present safe ways to launch, operate, and extend applications and services across Hybrid and Multi-Cloud environments. Securing these environments requires additional considerations:
Consistent Security Policies: Ensure that Security Policies are followed as practiced across the multiple cloud environments. To address the second issue, you should implement centralized management tools to put down policies and check compliance.
Inter-Cloud Security: Maintain a consistent but secure connection between various cloud regions or between an on-premise data center and a cloud provider. Ensure that information being sent to or received from other parties is protected while in transmission by employing secure and encrypted application programming interfaces.
Visibility and Monitoring: Monitor all cloud practices and log activities centrally for all the environments that the firm works with. Employable, use SIEM tools to gather intelligence data from different layers and store them to identify threats.
Conclusion
First of all, it is important to note that security of the cloud computing is an ongoing process that begins from the moment of its implementation and lasts at any stages of usage, along with constant emergence of new threats. Thanks to the proper adherence to the recommendations given in this article, organizations will be able to build a reliable and safe cloud environment that defended data from threats and simultaneously promoted business initiatives. Stay proactive, stay informed.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology
Exploring the Different Types of Cloud Computing

Exploring the Different Types of Cloud Computing
Introduction:
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals store, process, and access data and applications. It offers a range of services and deployment models that cater to different needs and requirements. In this article, we will delve into the various types of cloud computing, exploring their features, benefits, and use cases.
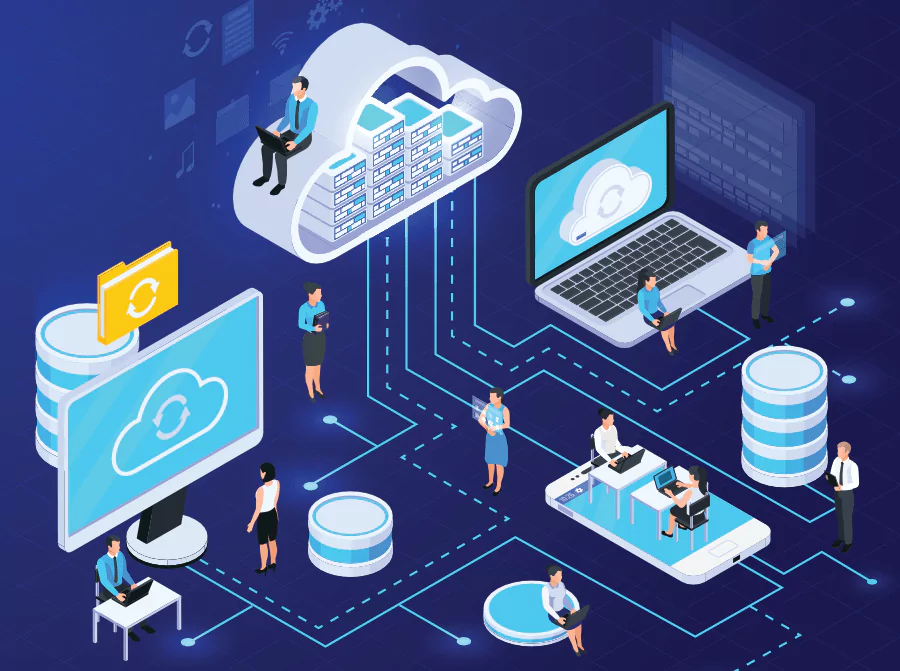

- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that revolutionizes the way organizations manage and deploy their IT infrastructure. In this model, essential computing resources, including virtual machines, storage, and networking components, are delivered over the internet, empowering users to create and control their IT environments remotely. Here’s a detailed breakdown of Infrastructure as a Service:
Key Features:
- Virtualized infrastructure components (servers, storage, networks)
- Flexible scaling options
- Pay-as-you-go pricing model
- Self-service management capabilities
Use Cases:
- Development and testing environments
- High-performance computing (HPC)
- Disaster recovery and backup solutions
- Scalable web hosting
- Virtualized Computing Resources: IaaS provides access to virtualized computing resources, allowing users to deploy virtual machines (VMs) tailored to their specific needs. These VMs simulate physical hardware, enabling users to run applications, host websites, or perform data processing tasks without investing in physical servers.
- Storage Solutions: IaaS offerings include storage solutions that enable users to store and manage data in the cloud. Users can leverage scalable and reliable storage options to accommodate varying data requirements, ensuring flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Networking Infrastructure: IaaS providers furnish networking infrastructure, facilitating the establishment and management of virtual networks. Users can configure network settings, such as IP addresses, subnets, and firewall rules, to ensure secure communication between virtual resources and external networks.
- Self-Service Provisioning: One of the key features of IaaS is self-service provisioning, empowering users to provision and configure computing resources independently. Through web-based interfaces or APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), users can rapidly deploy VMs, allocate storage, and configure networking resources according to their requirements.
- Scalability: IaaS platforms offer scalability, allowing users to scale computing resources up or down dynamically based on demand. Organizations can adjust resource allocations in real-time to accommodate fluctuating workloads, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Pay-As-You-Go Pricing: IaaS providers typically adopt a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where users are charged based on their actual resource consumption. This flexible pricing structure eliminates the need for upfront capital investments in hardware and enables organizations to align IT expenses with usage patterns, optimizing cost management.
- Resource Management and Monitoring: IaaS platforms provide tools for resource management and monitoring, enabling users to track resource utilization, monitor performance metrics, and manage costs effectively. These tools facilitate proactive management and optimization of IT infrastructure, enhancing operational efficiency.
- High Availability and Reliability: IaaS providers ensure high availability and reliability of infrastructure components by leveraging redundant hardware, data replication, and failover mechanisms. This ensures business continuity and minimizes the risk of downtime or data loss, enhancing the overall reliability of IT operations.
- Security and Compliance: IaaS platforms implement robust security measures to protect data and infrastructure from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. Providers adhere to industry-standard security practices and compliance regulations, offering features such as encryption, access controls, and threat detection to safeguard sensitive information.
- Disaster Recovery and Backup: IaaS solutions include disaster recovery and backup capabilities, allowing users to replicate data and applications across geographically distributed regions. This ensures resilience against catastrophic events and enables rapid recovery of IT services in the event of disruptions or outages.
In summary, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers a comprehensive suite of virtualized computing resources, storage solutions, and networking infrastructure delivered over the internet. By leveraging IaaS, organizations can achieve agility, scalability, and cost efficiency in managing their IT infrastructure, driving innovation and competitiveness in the digital era.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that facilitates the development, deployment, and management of applications without the complexities of infrastructure management. It offers a comprehensive platform that includes pre-built services, development tools, and runtime environments, empowering developers to focus on building innovative applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of Platform as a Service:
Key Features:
- Application development and deployment platform
- Built-in development tools and libraries
- Automatic scalability
- Multi-tenant architecture
Use Cases:
- Web application development and deployment
- Mobile application development
- Data analytics and processing
- Internet of Things (IoT) applications
- Complete Development and Deployment Environment: PaaS provides a comprehensive environment for application development and deployment in the cloud. It abstracts away the complexities of infrastructure management, allowing developers to focus solely on the application logic and functionality.
- Development Tools: PaaS platforms offer a wide range of development tools to support the entire software development lifecycle. These tools include integrated development environments (IDEs), code editors, version control systems, debugging tools, and collaboration features, enabling developers to write, test, and debug code efficiently.
- Pre-built Services: PaaS platforms come with a variety of pre-built services and components that developers can leverage to enhance their applications. These services may include databases, messaging queues, caching services, authentication services, and more. By utilizing these pre-built services, developers can accelerate development time and reduce the need for custom coding.
- Runtime Environments: PaaS provides runtime environments that support the execution of applications developed on the platform. These environments include programming language runtimes, middleware components, and application servers optimized for performance and scalability. Developers can deploy their applications to these runtime environments with ease, ensuring consistent performance across different deployment environments.
- Automated Scaling and Management: PaaS platforms often include built-in capabilities for automated scaling and management of applications. They can automatically adjust resource allocations based on application demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. Additionally, PaaS platforms handle routine maintenance tasks, such as software updates, patching, and monitoring, freeing developers from administrative burdens.
- Multi-Tenancy and Isolation: PaaS platforms support multi-tenancy, allowing multiple users or organizations to share the same underlying infrastructure while maintaining isolation and security between tenants. This enables efficient resource utilization and cost-sharing among users without compromising security or performance.
- Integration and Interoperability: PaaS platforms offer integration and interoperability capabilities, allowing developers to seamlessly connect their applications with other services and systems. They provide APIs, web services, and integration tools to facilitate communication between applications and external resources, enabling interoperability in complex IT environments.
- Vendor Lock-in Mitigation: PaaS platforms strive to mitigate vendor lock-in by adopting open standards and supporting portability across different cloud environments. They enable developers to build applications using standard programming languages, frameworks, and APIs, reducing dependence on proprietary technologies and easing migration between cloud providers if necessary.
- Security and Compliance: PaaS providers implement robust security measures to protect applications and data hosted on their platforms. They adhere to industry-standard security practices and compliance regulations, offering features such as data encryption, access controls, identity management, and security monitoring to safeguard sensitive information.
- Cost Efficiency: PaaS offers a cost-effective approach to application development and deployment by eliminating upfront infrastructure investments and providing pay-as-you-go pricing models. Developers can scale resources based on demand, optimizing cost management and maximizing return on investment (ROI) for their applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides users with access to software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. It offers a convenient and cost-effective alternative to traditional software deployment models, eliminating the need for users to install, manage, and maintain applications on their local devices. Here’s a detailed breakdown of Software as a Service:
Key Features:
- Fully hosted and managed applications
- Subscription-based pricing
- Automatic updates and maintenance
- Broad accessibility
Use Cases:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Human Resource Management (HRM)
- Collaboration and productivity tools
- Subscription-Based Access: SaaS delivers software applications to users on a subscription basis, typically charged on a recurring basis (monthly or annually). Users subscribe to the service and gain access to the software through a web browser or dedicated client software, without the need to purchase perpetual licenses or install software locally.
- Centralized Hosting and Management: SaaS applications are centrally hosted and managed by the service provider in the cloud. The provider is responsible for maintaining the underlying infrastructure, managing software updates, ensuring high availability, and addressing security concerns. This relieves users of the burden of software installation, configuration, and maintenance tasks.
- Accessibility and Cross-Platform Compatibility: SaaS applications are accessible from any device with an internet connection and a compatible web browser or client software. Users can access the software from desktop computers, laptops, tablets, or smartphones, enabling flexibility and productivity across different devices and operating systems.
- Ready-to-Use Applications: SaaS offers ready-to-use applications that are fully functional and feature-rich out of the box. Users can immediately start using the software without the need for extensive setup or configuration. This accelerates time-to-value and reduces the time and effort required to deploy and adopt new software solutions.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SaaS applications are inherently scalable, allowing users to scale usage up or down based on changing needs and requirements. Providers offer flexible subscription plans that accommodate varying user counts, feature sets, and usage levels, enabling organizations to align software expenses with business growth and fluctuations in demand.
- Automatic Software Updates: SaaS providers handle software updates and upgrades seamlessly, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features, improvements, and security patches. Updates are deployed centrally by the provider, eliminating the need for users to manually download, install, and manage updates on their devices.
- Data Security and Compliance: SaaS providers implement robust security measures to protect user data and ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards. They employ encryption, access controls, authentication mechanisms, and other security features to safeguard sensitive information and mitigate security risks.
- Customization and Integration: SaaS applications often support customization and integration capabilities, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs and integrate it with other systems and services. Providers offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), webhooks, and integration tools to facilitate seamless interoperability with third-party applications and data sources.
- Service-Level Agreements (SLAs): SaaS providers typically offer service-level agreements (SLAs) that define the level of service availability, performance, and support guaranteed to users. SLAs specify uptime guarantees, response times for support requests, and other performance metrics, providing users with assurance of service reliability and accountability from the provider.
- Cost Efficiency and Predictability: SaaS offers cost-efficient and predictable pricing models, with subscription fees based on usage, feature tiers, or user counts. Users benefit from predictable recurring expenses, avoiding upfront capital investments and reducing total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to on-premises software deployment models.
- Function as a Service (FaaS):
Function as a Service, also known as serverless computing, allows developers to execute code in response to events or triggers without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. FaaS abstracts away servers and infrastructure management, focusing on executing discrete functions. Developers write and deploy individual functions, and the cloud provider takes care of scaling and resource allocation.
Key Features:
- Event-driven computing model
- Auto-scaling and pay-per-use
- Reduced operational overhead
- Granular function-level control
Use Cases:
- Real-time data processing
- Microservices architecture
- Internet of Things (IoT) applications
- Chatbots and voice assistants
- Desktop as a Service (DaaS):
Desktop as a Service offers virtual desktop environments that are hosted and managed in the cloud. It enables users to access their desktops and applications remotely from any device with an internet connection. DaaS provides a consistent and secure desktop experience, allowing organizations to centralize management and improve data security.
Key Features:
- Virtual desktop infrastructure
- Device and location independence
- Centralized management and security
- Scalable and flexible desktop provisioning
Use Cases:
- Remote work and telecommuting
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies
- Resource-constrained devices
- Software testing and development environments
Conclusion:
Cloud computing encompasses a diverse range of services that cater to different user needs. Whether you require infrastructure resources, a development platform, fully managed applications, event-driven functions, or virtual desktop environments, the cloud offers a solution. Understanding the various types of cloud computing models is crucial for businesses and individuals to leverage the right services, optimize resource allocation, and drive innovation in the digital era.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

The Rise of Edge Computing: Processing Power Takes a Step Closer to the Action
The digital world is undergoing a tectonic shift. Data, once confined to centralized servers, is now exploding at the edges of the network, closer to where it’s generated and consumed. This decentralized approach, powered by edge computing, is poised to revolutionize industries from healthcare to manufacturing, and reshape the way we interact with technology.
Before we delve into the rise of edge computing, let’s rewind a bit. Traditionally, all our data – from sensor readings in factories to online transactions – traversed long distances to reach centralized data centers for processing. This centralized model, while effective for its time, presented limitations. Latency, the time it takes for data to travel and be processed, became a bottleneck, especially for real-time applications. Additionally, bandwidth constraints and security concerns added further complexities.
Enter edge computing – a paradigm shift where processing power is distributed closer to the data source, at the network’s edge. This empowers devices like smart sensors, IoT gateways, and even edge servers to process data locally, before sending it to the cloud or a central hub.
Imagine a factory equipped with edge-enabled sensors monitoring equipment health in real-time. Instead of sending this data to a central server for analysis, the edge device can detect an anomaly and trigger predictive maintenance, avoiding costly downtime. In a smart city, edge-powered traffic cameras can analyze traffic patterns in real-time, optimizing traffic lights and reducing congestion. These are just a glimpse into the vast potential of edge computing.
The Driving Forces Behind Edge Computing’s Rise:
Several factors are propelling the rise of edge computing:
- The Internet of Things (IoT): The explosion of connected devices, from smart homes to wearables, generating data at the edge, necessitates local processing for faster response times and improved efficiency.
- 5G and Low-Latency Networks: The advent of 5G with its ultra-fast speeds and low latency further fuels the edge computing wave by enabling seamless data transfer between devices and edge servers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms deployed at the edge can analyze data in real-time, enabling faster decision-making and intelligent automation at the device level.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Edge computing can address data security and privacy concerns by minimizing data transfer to central servers, potentially reducing the attack surface and enhancing data sovereignty.
Benefits of Edge Computing:
The benefits of edge computing are numerous and far-reaching:
- Reduced Latency: Processing data locally significantly reduces latency, critical for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
- Improved Bandwidth Efficiency: By filtering and pre-processing data at the edge, less data needs to be sent to the cloud, reducing bandwidth requirements and costs.
- Enhanced Scalability and Reliability: The distributed nature of edge computing makes it more scalable and resilient to outages or failures in centralized systems.
- Increased Decision-Making Speed: Local processing empowers devices to make real-time decisions, enabling faster responses and improved operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: Edge computing keeps sensitive data closer to its source, potentially reducing the risk of security breaches and unauthorized access.
Challenges and Future of Edge Computing:
Despite its immense potential, edge computing faces some challenges:
- Complexity of Management: Managing a distributed network of edge devices requires robust tools and automation capabilities.
- Resource Constraints: Edge devices often have limited processing power and storage, demanding efficient algorithms and resource optimization techniques.
- Security Concerns: Securing edge devices and protecting sensitive data at the edge remains a critical challenge.
However, the future of edge computing is bright. Advancements in chip technology, edge-optimized software, and innovative security solutions are continuously addressing these challenges. As research and development intensify, we can expect to see:
- Wider adoption across industries: From healthcare and manufacturing to retail and agriculture, edge computing will find applications across diverse sectors.
- Emergence of intelligent edge devices: Edge devices will become increasingly intelligent, capable of running complex AI and ML algorithms locally.
- Edge-to-cloud collaboration: A seamless interplay between edge and cloud will optimize data processing and enable efficient resource utilization.
In conclusion, the rise of edge computing marks a new era in the digital landscape. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing opens up a world of possibilities for faster, more efficient, and intelligent applications. As technology evolves and challenges are overcome, edge computing is poised to revolutionize the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

Artificial Intelligence: The Engine Powering Modern Enterprises
The once-futuristic vision of Artificial Intelligence (AI) seamlessly integrated into daily life is no longer a distant dream. The present landscape of modern enterprises is rapidly evolving, fueled by the transformative power of AI. From streamlining operations to forging cutting-edge innovation, AI has become the engine propelling organizations towards agility, efficiency, and success. This article delves into the multifaceted influence of AI within modern enterprises, exploring its applications, benefits, and the challenges that lie ahead.
We are on the cusp of a revolution that will fundamentally change the way we live, work, and think. And at the heart of this revolution is artificial intelligence…
Revolutionizing Enterprise Operations:
At the core of AI’s impact lies its ability to redefine operational efficiency. Repetitive tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and customer service inquiries are finding solace in the tireless hands of AI-powered automation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) understands customer queries, chatbots provide instant support, and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms automate data analysis, freeing up human resources for higher-level tasks. This shift not only minimizes errors and saves time but also allows employees to focus on strategic decision-making, customer engagement, and creative endeavors.
Boosting Customer Experience:
AI is not just about internal optimization; it is also reshaping how enterprises interact with their customers. Personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing models, and predictive maintenance capabilities empower businesses to create unique and tailored experiences. Imagine a clothing store suggesting outfits based on your past purchases and personal style, or a car manufacturer predicting potential issues before they even arise. AI fosters deeper customer understanding, builds loyalty, and drives profitable relationships.

Fueling Innovation and Growth:
Beyond streamlining existing processes, AI opens the door to unprecedented innovation. Research and development are being expedited by AI-powered algorithms that analyze vast datasets, generate new ideas, and predict market trends. Industries like healthcare are utilizing AI to analyze medical images, predict disease outbreaks, and personalize treatment plans. In the realm of product development, AI assists in designing novel prototypes, optimizing manufacturing processes, and identifying new market opportunities. This transformative power paves the way for groundbreaking solutions and sustained growth.
The Challenges of Integrating AI:
While the benefits of AI are undeniable, embracing its potential comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing ethical concerns around data privacy and ensuring transparency in AI decision-making processes are crucial considerations. Additionally, upskilling and reskilling the workforce to adapt to a changing landscape is essential. The fear of job displacement due to automation needs to be addressed through effective training programs that equip employees with the skills necessary to thrive in an AI-driven future.
The Future of AI in Enterprises:
Despite the challenges, the future of AI in modern enterprises is undeniably bright. Continuous advancements in AI technology, coupled with evolving regulations and a focus on responsible implementation, will pave the way for deeper integration and broader societal benefits. With a keen focus on human-AI collaboration, enterprises can leverage the power of AI to achieve unimaginable heights, fostering a future where machines augment human capabilities and drive advancements across all industries.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, AI is not merely a technological trend; it is a transformative force reshaping the very essence of modern enterprises. By embracing its potential while addressing the accompanying challenges, organizations can unlock a future of streamlined operations, enhanced customer experiences, and groundbreaking innovation. As we move forward, the key lies in harnessing the power of AI responsibly, creating a collaborative environment where humans and machines work together to drive progress and unlock the full potential of this transformative era.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

Cloud Migration Strategies: Moving Your Infrastructure to the Cloud
Introduction:
Cloud computing has changed how organizations manage and deploy their IT infrastructure. This was mainly because of the flexibility, high scalability, and cost efficiency in cloud services—features most view as befitting any organization’s size. However, migration of existing infrastructure to the cloud requires good planning and execution. This paper explains the critical cloud migration strategies that an organization can adopt to make moving from an existing environment to the cloud environment smooth and successful.
Cloud migration is almost similar to the organizational change experience in the organization; thus, it needs a roadmap, planning, and preparation with care. It is not a simple lift-and-shift operation; it requires an in-depth analysis of the current infrastructure, proper choice of the cloud model, setting clear goals, planning for data migration, dealing with security and compliance, thorough testing and validation, controlling change during the migration process, and, more important, continuous optimization post-migration. Migration should be all-inclusive; therefore, it guarantees a smooth and efficient method based on organizational needs and strategic objectives.
Cloud Migration Strategies
Analyzing Current Infrastructure
Before doing anything on cloud migration processing, review what you already have in your infrastructure: identify applications, servers, databases, and data storage systems to be migrated. Note dependencies, performance requirements, and security needs for each element. Such an initial assessment eases your understanding of the scope and possible challenges that could come along in the migration process.
Inventory Detail:
Develop detailed inventory that comprises all the IT assets that are currently operational in your infrastructure: hardware, software, applications, and data storage systems. For each asset, it is essential to detail the specifications, current usage, dependencies, and performance or security requirements of an application. These will reflect your foundation for a migration strategy since this is where you come to understand the size and scope of the project, as well as where potential pitfalls in the process might be found.
Analyze Dependencies
To be aware of the dependencies among different infrastructure components is another important task in a successful migration strategy. Find the applications that rely on some database, server, or other applications. This will help you effectively plan migration with minimum disruption and ensure that dependencies are all well catered for. Think of developing a dependency map that will display these relationships visibly so that steps can be planned for how migration is carried out in sequence.
Evaluation of Performance Requirement:
Every component of the infrastructure has its set of requirements that have to be met from the point of performance within the cloud. Dwell into the current performance level of the applications and identify the cloud resources required to add for maintaining the existing performance level or maybe increasing the performance level: CPU, memory, storage, and network bandwidth. Thus, you can pick the correct set of cloud services along with the correct configuration to achieve post-migration optimal performance.
Identifying the Security Needs:
One of the most critical criteria for cloud migration is security. Determine all security requirements for each infrastructure component, including data encryption, access controls, and conformation with industry standards. Compare existing security functions across different cloud service providers to ensure that those security functions will be in line with organizational requirements. Probably, one should take a risk analysis on the security component to identify potential threats and develop mitigation strategies.
Picking the Right Cloud model
The selection of the right cloud model is the key to the successful cloud migration. The public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud models respectively provide flexibility and much lower costs; exceptional and tough security with more ease of control; and the best of both worlds. This decision will be made based on the requirements and priorities of an organization. Public, Private and Hybrid clouds explained Public Cloud: The public cloud is a shared infrastructure that provides economies of scale and improves efficiency. It is the managed collection of services and resources provided by third-party cloud service providers. It allows organizations to dynamically grow resources when they are needed, and reduce those same resources when they are not, and organizations pay only for what they really need. Public clouds are ideal for applications with variable workloads, such as web hosting, development, and testing environments.

Private Cloud: A private cloud is a dedicated infrastructure that offers enhanced security and management. Normally, it is sited within an organization or at a third-party data center but run by the company itself or other providers, making them good for applications with strict compliance and security demands like those found in healthcare, government agencies and financial services. It gives more control over information and infrastructure to secure sensitive information.
Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud encompasses the advantages of public and private clouds enabling organizations to enjoy benefits of both. Thus, it allows integration between on-premises resources and off-premise ones which facilitates scalability as well as flexibility while retaining control on data privacy issues. They are suited for organizations that want to balance their security needs as well as performance against cost savings and agility.
Evaluating Organizational Needs and Priorities:
The choice of which model to adopt should be based on what an organization wants. The following are some factors to consider when assessing cloud models:
Security and Compliance: Find out about your application’s security requirements including your data protection obligations. Determine if its public, private or hybrid model can best meet these requirements.
Migration Goals and Priorities Establishment
When migrating to the cloud, set up well-defined goals and objectives. Do you have plans to reduce costs? You could be in desperate need for scalability or agility. This will make it possible to set goals, determine when the decisions should be made and tasks prioritized.
Defining Specific Migration Objectives:
What are your specific migration goals in relation to this project? These objectives must coincide with organizational strategies as well as addressing business requirements. They may include:
Cost Reduction: Cloud migration is aimed at reducing costs in the IT department. The areas that this deals with include reducing infrastructure costs, lowering maintenance expenses and decreasing operational costs. Organizations can leverage pay-as-you-go models offered by the cloud while avoiding expensive hardware and software investments.
Scalability and Flexibility: The cloud provides organizations with an unmatched ability to scale their resources depending on demand. Some firms experience fluctuations of workloads while others see seasonal peaks.
Agility and Innovation: An organization’s agility can improve due to moving into the cloud environment. With these services accessed from the platform, any enterprise can rapidly launch new applications & services, adapt itself to market changes thus outperforming its rivals by reaching new business areas
Setting Priorities and Timelines:
Once you have defined migration goals, you should prioritize them based on their importance and the impacts they are likely to have on your organization. Make a migration project timeline by noting all major milestones and deadlines. This will ensure that the process of migration is kept in line and resources are distributed efficiently.
Involvement of Stakeholders:
Do involve executives, IT teams, and business units as key stakeholders in the planning stages of migration. Get their ideas so that the objectives for migration fit into an overall organization’s strategy and address the needs of all affected parties. Such an inclusive process will create support for this project and make it a success.
Data Migration Planning:
One must carefully plan how to move data since it’s one of the most critical assets that shall be transferred to a safe location. Look at how much there is, its structure, and sensitivity. Choose a good method of moving it between on-premises infrastructure or cloud infrastructure: thus either lift-and-shift or refactored approach used to re-engineer applications for optimization purposes in cloud computing implementation. Ensure data integrity and security throughout the entire moving process.
Assessing Data Volume & Structure:
Start by assessing how much data needs to be migrated. This involves identifying what types of data would be such as structured, unstructured or semi-structured ones; Understanding the data’s characteristics will help you choose the most appropriate migration approach and tools.
Choosing the Right Migration Approach:
There are several approaches to data migration, each with its advantages and considerations:
Lift and Shift: The process of lift and shift encompasses transferring current applications and data to the cloud without changing the underlying structure. This method is relatively fast and easy, although it may not make use of all the potential advantages that come with the cloud. This is a good fit for applications requiring minimal modifications that can run effectively in a cloud environment.
Replatforming: Replatforming means making slight adjustments to applications to make them suitable for the cloud. It might involve updating operating systems, databases, or middleware in order to take advantage of Cloud-native services. By enhancing performance and scalability while keeping disruptions on already existing apps at a minimum, replatforming helps.
Refactoring: Refactoring alternatively called rearchitecting involves redesigning applications in such a manner that makes them work with native features of clouds. This will require significant changes to application architecture as well as code but can lead to improved performance, scalability and cost effectiveness thereafter. Refactoring is perfect for those applications which are meant either to be updated or have complex requirements which cannot be satisfied by using lift-and-shifts or replatformings.
Hybrid Migration: Sometimes, organizations have to hybridize their migrations thus they will just move some components with the lift and shift approach while others have to be refactored. This is a flexible strategy that allows companies to go to the cloud with time and also meet specific requirements and limitations.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Security:
For this reason, data integrity and security should be maintained when moving data from one system or platform to another. To guarantee secure and successful data migration use the below best practices:
Data Encryption: Encrypt information at rest and in transit so that unauthorized people cannot access it. Employ robust encryption algorithms as well as manage encryption keys securely.
Access Controls: The process includes tight access controls restricting access to data for modification during migration. Role-based access control (RBAC) is important in ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.Data Validation: Perform validation checks on data before, during, and after migrating it to ensure that all records are transferred accurately and completely. Use automated tools for identifying any inconsistencies or errors existing within these datasets.
Compliance: It is essential that the migration aligns with applicable industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS etc., hence work closely with your service provider to understand what compliance capabilities and ensure that your data remains protected.
Backup and Recovery: Create backups of critical data before starting the migration process. This ensures that you have a recovery plan in case of any issues or data loss during migration. Test the backup and recovery procedures to verify their effectiveness.
Addressing Security and Compliance:
Guarantee high security while migrating to the cloud. Identify potential risks in security and implement the appropriate access controls, mechanisms of encryption, and security protocols. Enforce industry-specific regulations and standards for the protection of data and compliance. Interface with the cloud service providers to understand the security measures and ensure a secure migration.
Identifying Security Risks:
Start by recognizing possible cloud migration risks. Such perils hold the data breaches, unauthorized entry, loss of data and violation of compliance. Carry out a comprehensive risk assessment on security to identify vulnerabilities as well as come up with ways of mitigating them. You might also use threat modeling techniques to understand how the entire infrastructure can be attacked and how this could affect it.
Access Controls Implementation:
During the migration process, institute strict access controls for protecting sensitive information and applications. Utilize role-based access control (RBAC) so that key resources can only be accessed by authorized personnel. Abide by least-privilege principles to limit users’ authority to the minimal level required in order to perform their roles sufficiently. Regularly review access controls and keep them up-to-date for effectiveness purposes.
Encrypt data in all its states to protect it from unauthorized access. Utilize strong encryption algorithms and keep your encryption keys safe. Secure the communication between on-premises infrastructure and cloud by means of SSL/TLS protocols. Consult with your cloud service provider about their encryption capabilities and make sure that data is continuously protected during the migration process.
Security Protocols and Best Practices:
Deploy security protocols for protecting your environment while migrating. These include multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular software updates and patching, network traffic monitoring for suspicious activities as well as intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS).
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements:
Ensure that you conform to regulations specific to your industry like GDPR, HIPAA or PCI-DSS. Regularly audit your infrastructure but also understand what compliance capabilities exist with regard to a particular cloud service provider.
Testing and Validation:
Design testing applications and infrastructure to performance, functionality, and compatibility. Perform load, stress and security tests to make sure the new one can withstand the workload.
Performance Testing:
Do Performance testing to take care of expected loads Leverage performance monitoring tools to record and manage those magical metrics.
Functionality Testing:
Test services and applications in your handshake script. Use the Testing tools like Autotest to expedite this process.
Compatibility Testing:
Verify Application and infrastructure to be cloud ready. Compatibility Issue Resolution
Security Testing:
Spot potential weaknesses, and address them. Penetration testing and Vulnerability scanning.
Managing Change and Training:
Deploy a change management strategy and so train IT teams and end-users on how to work in the new cloud environment. Address Migration Concerns and Migrations Headache
Change Management Strategies:
Be sure to create a change management plan and make it known to everyone involved. Keep all parties informed on a regular basis, and ensure that any issues or questions are dealt with promptly.
Training and Support:
It is important to provide comprehensive training and support; this can be done through hands-on training sessions as well as workshops that are supplemented with ongoing support mechanisms.
Engaging End-Users:
Involve end-users in the planning and decision-making processes; gather feedback from them regularly and keep them updated on any developments that take place.
Continuously Monitoring and Optimizing:
After the migration, deploy monitoring tools to keep track of performance metrics such as scalability and cost implications of the cloud resources being used; ensure an optimization effort is carried out alongside efforts towards cost management.
Implementing Monitoring Tools:
Use cloud-native monitoring services to collect and analyze metrics, logs, and events. Implement application performance monitoring (APM) tools to gain insights and identify areas for improvement.
Optimizing Cloud Resources:
Regularly evaluate and optimize your cloud resources to ensure efficient and cost-effective usage. This includes resizing instances according to workloads, dynamically adjusting resources based on demand using auto-scaling, employing cost management tools that can monitor spending habits and so on. Develop resource tagging policies as well as allocation policies which will ensure that resources are used appropriately and align with organizational goals.
Performance Tuning:
Always work toward the best performance and minimize downtime in the cloud by constantly making your cloud infrastructure better. Tweak your configurations, re-optimize database queries, tighten up your code to make your responses lightning fast. Find bottlenecks by monitoring and use those monitoring tools to improve the performance if possible and change them everywhere to make the performance better. Cost Management: Cost management strategy to monitor and manage cloud spending and optimize spend. For example, use cost management tools to monitor spending, create budgets and maintain use rate limits, and implement cost reduction concepts such as reserved instances, spot instances and savings plans. Continuous cloud usage billing optimization for investment maximization.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:
Establish a robust disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity (BC) strategy using cloud-native services for backup and replication to ensure data redundancy and minimize downtime during disasters. Regularly test recovery mechanisms to validate their effectiveness.
Developing a Disaster Recovery Plan:
Disaster Recovery Plan Creation: Establish a disaster recovery plan that defines recovery steps and processes from start to finish. Determine what is important to you, establish your recovery time objectives, and then go and define a backup and replication strategy for those applications and data. Use cloud-native services: Implement backup and replication strategies by using cloud-native services (e.g., AWS Backup, Azure Site Recovery or Google Cloud Backup ). These solutions are managed secure services designed to provide automated, scalable data protection and disaster recovery, enabling robust data availability and recoverability. Multi-Region Replications – It mainly focuses to provide redundancy against data loss.
Testing Recovery Mechanisms:
It is vital to regularly test disaster recovery mechanisms, which plays a key role in its reliability. Do not neglect failover tests alongside recovery drills and simulations ᅳ these are essential to validate the recovery procedures that have been put in place and also to pinpoint the missing links. Document all the details of the test results; this will enable you to easily identify what adjustments should be made on the disaster recovery plan. Take all necessary precautions.
Ensuring Business Continuity:
Carry out a detailed business continuity plan that encompasses all areas of operation. Define the critical business functions, set recovery goals and identify appropriate communication channels plus other coordination procedures. Make sure to deploy cloud-based services such as virtual desktops and collaboration tools: these facilitate remote work and make it easy to achieve business continuity whenever there are interruptions.
In the spirit of after-migration analysis and optimization:
Post-migration, a post-execution survey will be done to give an accurate evaluation of the success. This is done in order to come up with the stakeholders’ views plus their interests on the areas that need to be optimized further. On a regular basis, re-examine the efficiency and cost of cloud infrastructure services and factors contributing towards itᅳ including securityᅳ taking the requisite corrective actions for enhancement. These are some of the best practices to ensure continuous improvement after migration.
Evaluating Migration Success:
Perform a post-migration assessment to rate the success of the migration project. Collect feedback from stakeholders, performance stats, and assess the results compared to the goals you had set out pre-migration. Pinpoint areas of weakness and create strategies to rectify them For collecting stakeholder feedback & input, Involving stakeholders in the post-migration evaluation process. Survey, Interview and conduct focus groups to learn more about their experiences, and the challenges. Use the feedback to hone your cloud infrastructure. Continuous Improvement: Create a cycle for continuous improvement to fine tune cloud infrastructure. Continually retesting performance, cost, and security measures, adjusting where necessary to improve efficiency and effectiveness Put a process in place to monitor and iterate on the cloud infrastructure to meet ever changing business needs.
Conclusion:
Cloud migration however is a very strategic and complex process with well-planned and well-executed migration activities and managing the migrated platform. The best practices for doing this are to follow the established paradigms for scaling, measuring, and operating infrastructure in the cloud efficiently and cost-effectively. There will still need to be some work put into measuring infrastructure, moving the data and security over, testing that it all works and everyone can still do their jobs, managing the change and ongoing operational optimisation. Research Criteria: Cloud computing is a broad topic but these candidates have additional eligibility requirements to ensure fact-based insight. Data Sources: The global cloud computing market was valued at $3 Fact-based insights on the global cloud computing market which was valued at $371. These numbers show the significance of data security, with the global cloud security market expected to rise to $8.9 billion by 2026.
Engaging Anecdote:
Ponder your present infrastructure. Imagine the city where there are always heavy flows of vehicles and old buildings to be renovated. Switching to the cloud is something similar to changing the address to the beautiful gated neighborhood, with the river of cars freely moving among sophisticated architectural masterpieces. Allowing for such a shift is a subtle undertaking as the creation of a new city with numerous components being synchronized with precision.
Posting your first step in the cloud migration process is like setting sail. It would be most important to assess your current configuration by checking its effectiveness, then choose the right model for cloud in relation to the evaluation and plan on how data will be transferred—wherever, it is, and security measures. While transiting through test and validation, it is essential to ensure that the team is knowledgeable and actively learning as it is a key factor in determining set operational efficiency and safety of the new environment being adopted. Monitor it continually post-deployment.
A mid-sized firm has gone to the cloud system and they need it just recently. After identifying the business applications and mapping their dependencies, they had selected the suitable model of the hybrid cloud to get the balance between freedom and security. It is from this choice that other migration goals were made clear and sharp to focus on what was relevant, and a choreographed data migration leaving no doubt of data relied on.
They have successfully tackled issue-areas relating to security, conducted tests and have continued to train and support migrating systems for best results.
Why Cl Migration Matters: This position was evolved by undertaking comprehensive studies on the specialized topic of fashion designing and by selecting the best characteristics of desirable employees.
However, it will be important to understand that cloud is trending in the current world and getting adoption from organizations is unavoidable. Hence, the cause of high applicability of the concept of effectiveness, the fact that it is low cost and available enhances its importance. Cloud migration strategies become beneficial to an organization as it assists the organization in redesigning its functions and make them more efficient for the change and flexibility is paramount in today’s world.
Final Thoughts:
Cloud migration is a highly effective change that can be instrumental in fundamentally reorienting your organization’s IT landscape. The design and planning for security and performance of the system will address such issues and lead to a sound plan for the setup of a sound security system as a stable and healthy framework for the future. Embrace the spirit of migration to transform and evolve your business. So always recall that the cloud is not just an end point, but a journey toward a flexible and fabric-based IT future.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

Cloud Computing: Empowering the Digital Age
Introduction:
As a new technological innovation in the era of networking, cloud computing has become a central technology that revolutionizes the accessibility, storage, and processing of data in today’s organizations and society. Cloud computing is self-service over the Internet offering storing and processing resources for demonstrated usage to realize practical business value. This article seeks to understand cloud computing to embrace it as a fast-moving technology that has different features and effects that pose some advantages and challenges to different sectors.

Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a model for computing that brings computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, applications, software and networks available to the user over the internet. This removes the requirement of local infrastructure as access is granted to appointed shared resources located in the server. These resources can be obtained and used on a need by need basic; hence it is very flexible in its usage because organizations are in a position to pay for what they develop as per their needs for computing power, and storage capacity. The delivery of cloud services is done by three main methods: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These models each present different ways of addressing user requirements while still meeting them at some level or another.
When a company outsources its IT infrastructure from a vendor or cloud service provider in order to use what is called Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), they are participating in ‘Infrastructure as a Service’ (IAAS). This type of Cloud Computing allows businesses to rent space on servers where they can store data about themselves and others securely – without having any physical equipment at home. This model enables the business to hire servers as well as storage spaces at a very flexible and affordable charge without having to go through the rigorous process of acquiring the physical equipment. The clients have a certain control over the operating systems, the application and the development environments but the cloud provider is a)responsible for the infrastructures.
Illustrations of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Service, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. These platforms provide wide array of services which includes Virtual machines, Block storage and Networking components. Organizations can easily allocate these sources depending on its requirements and might effortlessly growth or decrease them as according to the requirement – a aspect that increases the flexibility of an organisation from owning physical devices.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is a model which gives customers with a platform for growing, strolling, and web hosting their packages while being free from the responsibility of coping with the real hardware. This ranges from physical servers, storage, networks, and databases as well as the software defined equivalents thereby allowing the developers to concentrate more on writing code and deploying applications. PaaS is easier to use and quicker in the development processes since the provider has already preset typical environments and tools.
Some of the well-known PaaS solutions are Heroku, Google integrated Application Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Services. These platforms consist of integrated development environments (IDEs), Database management systems, and middleware that helps to ease the development process and provides shorter time periods for the development of new applications. PaaS is in particular beneficial for begin-usaand SMEs because it allows users to hastily installation and increase packages, in particular with out the want for high initial coins outlay for the purchase of device.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS entails the availability of software applications over the net, wherein the clients pay a subscription price to access the software program. Customers obtain a form of a software application on which they can run on their local devices through browser without having to install or maintain additional applications. This model provides a value proposition for end-user who needs to access different software solutions in order to solve their problems but who don’t necessarily have the resources to manage the software and hardware infrastructure to support them. Exemplary SaaS categories include customer relationship managers, web mail, and productiveness software.
Some renowned examples of SaaS include salesforce, Google workspace earlier known as G suite, and MS office 365. The functionality of these platforms varies from basic – e-mail, collaboration – to more complex such as analytics and even CRM. SaaS applications can be accessed anytime via the internet, which is quite beneficial, especially when working remotely or in a team spread across various geographical locations.
Global Data-on Demand is an organization that has embraced cloud computing as one of its exclusive service providers. It is critical to understand key characteristics of cloud computing that makes it attractive to organizations like Global Data-on Demand.
A lot of potential benefits have been associated with cloud computing based on its several key characteristics. Some of the common characteristics of Cloud Computing are as follows – Self Service – that too on demand; Multi-Tenancy; Infrastructure as a Service; Service Osborne & Hall (2012) stated that Cloud Computing has several key characteristics; these characteristics include on-demand self-service, access over the network, resource pooling, ‘elastic’ capabilities and that customers are billed for the amount of use.
On-Demand Self-Service
Cloud computing provides high utility and high flexibility because it can be accessed and used as a service without the need for assistance from a technical support person. Clients can effortlessly provision and use computing resources with the help of elegant web interfaces as well as APIs, which makes the process less time-consuming as compared to those that are dedicated to infrastructure.
For instance, the software developer or the engineering student may need to run a new application and instead of getting entangled with IT support, can create a virtual machine within minutes on AWS or GCP. This brings ability to innovate and new products into the market much faster among the advantages of using an agile process.
Broad Network Access
Autonomous system and software resources are shared over the Internet in a non-prescriptive fashion as a service rather than as a product. Writing this characteristic makes it possible that the cloud resource is availed in different places to enable the users to work effectively from remote areas.
This can be particularly beneficial to those organizations with employees located remotely. It means that instead of being limited to using computers at offices, employees can utilize their laptops, tablets or even smart phones in order to access company applications and data. This makes the operation to be efficient and also it help the businesses to get more talents from other countries.
Resource Pooling
Resource pooling is one of the fundamental principles of cloud computing, which means that multiple users are bonded to use the identical resources to reach optimum utilization. Multi-tenant models are commonly used by cloud service providers to assign and dynamically allocate resources depending on their usage to prevent resource wastage and encourage more efficient use of the resources in order to cut down on costs as much as possible not forgetting convenience in their process.
For instance, one actual physical server within using a data center, can host multiple virtual machines for use using various clients. Such a model of multitenancy enables cloud service providers to have efficient ways of pricing on the cloud as well as ensuring proper utilization of resources.
Rapid Elasticity
The cloud-computing architecture also provides quick elastic resource provisioning, which lets users increase or decrease allocated resources as necessary. This characteristic allows organization to be capable to plan on how best to meet new workloads and business needs with out a need to constantly overbuy or under-provide.
Pay-Per-Use Model
Pay-as-you-go model is another major strength of the cloud computing services; the utility is billed based on the amount of utility used. The system minimizes capital consumption during the initial phases of implementation and enables organizations to set their spending in correspondence to actual demand.
For instance, a firm with an ongoing marketing campaign can request extra computing assets in support of its promotional efforts and only be charged for the extra utilization. This flexibility makes it possible for businesses to plan well for their spending and avoid having huge infrastructure lying dormant and unproductive.
Impact of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing implies a wide range of changes as to various fields and industries, and as to the business models and people’s experience of using various kinds of services. It is seen operating in the business sectors, the health sector, and the educational sector enhancing the performance and efficiency.
Business Sector
The importance of cloud computing in the business sector cannot be overlooked due to the change it has brought to data storage and processing. From this point of view, organizations can store tremendous amounts of data in the cloud safely and eradicating physical infrastructure, and maintenance costs also are not an issue. In addition, cloud supported platforms can function at variable capacities and quickly add shipping solutions as per the dynamic business environment.
For instance, many streaming platforms such as Netflix use cloud computing to ensure that millions of clients are served appropriately. This implies that through this Cloud infrastructure, Netflix can manage its resources in a way to meet its changing demands of clients in viewing content.
The advancement of cloud computing has also promoted knowledge and cooperation in technology by offering a stable platform. This implies that through the use of tools and services that exist in cloud computing, developers are better placed to create and implement applications first time around. Further, cloud computing has led to the appearance of a new model in the provision of software, the Saas model that allows a user to use certain software through subscriptions without installing the applications.
Healthcare Sector
Cloud computing has emerged as a critical component of change in the areas of health by offering numerous health benefits for patients and researchers. That make it possible to store and share the patients’ Electronic Health Records in a secure manner and makes the handling of patients health records easier for the various health care providers. Additionally, analytics and machine learning solutions enable clinicians to gain great insights from the mountains of medical data, which helps diagnose and treat patients.
Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring are facilitated by cloud computing which makes it possible for the healthcare practitioners to extend services to patients who are in areas that are at a distance, or those that are not fully served. This accessibility also improves the quality of services delivered and makes it possible to provide solutions to distressing situations during calamities.
For example, during the COVID-19 crisis, most healthcare organizations embraced telemedicine techniques to continuing conducting remote sessions and checking on their patients without the need for physical contact. Platform-based solutions provided doctors an ability to address their patients remotely, including; reviewing patients’ records, video consultations, and prescribing drugs – all of which ensured patients received proper care without the risk of getting infected.
Education Sector
Cloud computing has acted as a revolution to education sector and has made it convenient to intake education for children all over the world especially through remote learning and collaborations. The different cloud platforms can be adopted to disseminate learning materials, course modules, and other resources, as well as learning resources and collaborative applications to students in educational institutions. In the current COVID-19 pandemic for instance, the system has continuously allowed education to be delivered with little disruption.
Learning management systems or also called Virtual learning environment, help the tutors to conduct the online tests, help in tracking the performance of the student and offer individual and differentiated learning experiences. Moreover, cloud computing helped in creating virtual classrooms and assisted educators to make their lessons informative and assertive despite the prevailing geographical barriers.
For example, Google Classroom and Microsoft Teams now cannot be considered as learning technologies but necessities in the classroom and student life. These platforms allow for real-time collaboration and activities including instant messaging and the upload and sharing of files, mimicking the classroom experience in a virtual space.
Compliance and Regulations
It is deemed essential for the organizations to pay attention to compliance with the trends encountered in organizations’ industries due to the existence of announced industry-specific standards for cloud computing. For instance, healthcare organizations/stakeholders are required to strongly embrace the Health Insurance Portability and we must implement the Healthcare and Insurance Accountability Act (HIPAA) to safeguard the information of patients. Establishments in the financial sector are bound by rules and regulations that relate to matters dealing with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) as well as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). There are strict regulations and violations of these can lead to many repercussions including severe penalties and Reputation – management risks.
Therefore, organizations ought to engage cloud providers and find out different ways of compliance. This entails assessing the provider in terms of his/her security measures, practices of handling and disposing of data and demonstrating his/her power of audit. Some of the certifications and attestations that are provided by some cloud providers are compliance certifications for services that meet the compliance benchmarks.
Internet Connectivity and Downtime
Dependence on the internet for the delivery of cloud services entails risks, including; Shortage of internet connection and connection interruptions. Such risks demand that organisations need to have a good backup and disaster recovery strategy in place. Such measures as having multiple connections to the network and having plans for fail-safe mechanisms can make it possible to have uninterrupted access to the services that are hosted in the cloud.
For example, an e-commerce organization that uses the internet and cloud services to host the business and its transactions must have a disaster recovery plan. Such a plan could mean always having an extra data center that a company can use if one becomes unavailable or using a couple of cloud services to implement the same.
Vendor Lock-In
It is however crucial to consider that by adopting cloud computing, an organization may be locked into their vendors. Ah, migrating from one cloud service provider to another is often a difficult and expensive process because the CSPs may be based on very different systems and architecture, use different API and data formats, and so on. Cloud providers need to be selected after careful consideration and more than one solution should be adopted such that if on cannot stick to one the other can be utilized to avoid being locked up.
For instance, a company which primarily relies on AWS as its primary cloud computing service provider may rely on GCP for additional services or as an AWS backup. This approach can help minimize risk, achieve diversification, protect against any monopolistic actions and ensure flexibility through working with different cloud providers.
Cost Management
Although using actual volumes is a cost cutting measure, still cost management in clouds can sometime be a daunting task. It is imperatively upon organizations that use these systems to ensure that they keep track of their usage and correspondingly strive to ensure that they manage their resources in ways that the costs that they are bound to incur are not unpredictable. Using cost management strategies and techniques, which include the establishment of costs, assessment of usage and optimization of the need for the resources, can go a long way in managing cost.
Here, we present some of the available tools at the disposal of cloud providers for metering cost in cloud environments. For instance, AWS has Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor that enables users to evaluate spending, and get tips on potential cost optimization opportunities. Organizations ought to ensure that they monitor their cloud consumption and optimization of resources to match the budgeted and organizational requirement.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the real deal, which made a difference in how companies run their operations, individuals consume services, and industries address challenges and opportunities. Thus, its potential for large-scale adoption, versatility and affordability have paved way for more innovative opportunities within different industries, enable digital innovation. However, security, legal and compliance, and possible risks are the concerns that organizations face in adopting the cloud solutions model. When it comes to its prospects, cloud computing is without a doubt a prounounced tned which refers to its ability to transform the world of Information Technologies further on as the technology progresses and new potentials of cloud services emerge.
This paper provides a brief overview of cloud computing definition, outlining its key characteristics, strengths as well as some of the major limitations or drawbacks while highlighting the need for organizations to strategize on how to best adopt this revolutionary innovation. Cloud computing will remain a dominant technology space, and its adoption is poised to grow in the future defining the course of business and other sectors in fields such as healthcare and education for the digital age.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology
Exploring the Internet of Things: Transforming the World with Connected Devices
Introduction: The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a groundbreaking technology that is revolutionizing the way we interact with our surroundings. With the ability to connect everyday objects to the internet and enable seamless communication and data exchange, the IoT is reshaping industries, enhancing efficiency, and transforming the world we live in. This article provides an overview of the Internet of Things, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding the Internet of Things: The Internet of Things refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity that enable them to collect and exchange data. These devices are interconnected and communicate with each other through the internet, enabling real-time monitoring, control, and automation of various processes.
Applications of IoT: The applications of IoT are vast and diverse, spanning across numerous industries. In the healthcare sector, IoT devices are used for remote patient monitoring, smart medical devices, and improving the efficiency of healthcare delivery. In transportation, IoT enables connected vehicles, intelligent traffic management systems, and logistics optimization. Smart homes utilize IoT to automate tasks, enhance security, and improve energy efficiency. Industrial IoT (IIoT) is revolutionizing manufacturing and supply chain management by enabling predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and process optimization. Agriculture, retail, energy, and many other sectors are also leveraging IoT to enhance productivity and deliver innovative solutions.
Benefits of IoT: The Internet of Things offers several key benefits. Firstly, it enhances efficiency by automating processes, optimizing resource utilization, and reducing human intervention. IoT enables real-time data monitoring, allowing for timely decision-making and preventive maintenance, which leads to cost savings and increased productivity. Additionally, IoT improves the quality of life through smart homes, wearable health trackers, and personalized services. It also enables greater sustainability by optimizing energy consumption, waste management, and environmental monitoring. Furthermore, IoT fosters innovation by enabling the development of new products, services, and business models.
In the digital era, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a groundbreaking technology, reshaping industries and revolutionizing the way we interact with the world around us. This article delves into the transformative power of IoT and its pivotal role in driving digital transformation across various sectors.
Understanding the Internet of Things
At its core, the Internet of Things refers to the network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to collect and exchange data. These devices can range from everyday objects such as smart appliances and wearable devices to industrial machinery and infrastructure.
The interconnected nature of IoT devices facilitates seamless communication and data exchange, paving the way for enhanced efficiency, productivity, and automation. By harnessing the power of IoT, organizations can gain valuable insights into their operations, optimize processes, and deliver innovative products and services to meet evolving customer demands.
Key Components of IoT
IoT comprises several key components that work together to enable connectivity and intelligence:
- Sensors and Actuators: These components serve as the eyes and ears of IoT devices, collecting data from the surrounding environment and initiating actions based on predefined parameters.
- Connectivity: IoT devices rely on various communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks to transmit data to centralized systems or other connected devices.
- Data Processing and Analytics: The vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices are processed and analyzed in real-time to extract meaningful insights. Advanced analytics techniques such as machine learning and artificial intelligence play a crucial role in uncovering patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms provide scalable storage and computing resources for managing IoT data, hosting applications, and facilitating remote device management.
- Security: With the proliferation of connected devices, ensuring robust security measures is paramount to protect against potential cyber threats and safeguard sensitive data.
Applications of IoT Across Industries
The impact of IoT spans across various industries, driving innovation and enabling new business models:
- Smart Cities: IoT technologies are instrumental in creating smart, sustainable cities by optimizing resource utilization, improving public safety, and enhancing urban mobility through connected infrastructure and intelligent transportation systems.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, IoT-enabled devices such as remote patient monitoring systems, wearable health trackers, and smart medical devices empower healthcare providers to deliver personalized care, improve treatment outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs.
- Manufacturing: IoT revolutionizes manufacturing processes by enabling predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring of equipment performance, and supply chain optimization. Smart factories leverage IoT technologies to enhance efficiency, quality control, and responsiveness to market demands.
- Agriculture: IoT solutions are transforming agriculture through precision farming techniques, automated irrigation systems, and crop monitoring sensors. By harnessing IoT data, farmers can optimize crop yields, minimize resource wastage, and mitigate environmental impacts.
Challenges and Concerns: While IoT brings tremendous opportunities, it also presents challenges and concerns. Security and privacy are major considerations, as interconnected devices can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks and unauthorized access. The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices raises concerns about data privacy, storage, and ownership. Interoperability and standardization issues can hinder seamless communication between devices from different manufacturers. Furthermore, the rapid proliferation of IoT devices necessitates robust network infrastructure and bandwidth capabilities.
Future Outlook: The Internet of Things is poised for exponential growth in the coming years. Advancements in connectivity technologies, such as 5G, will enable faster and more reliable communication, facilitating the widespread adoption of IoT devices. Edge computing will play a crucial role in processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making capabilities. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will be integrated with IoT, enabling autonomous systems, predictive analytics, and intelligent automation. As the IoT ecosystem expands, businesses will continue to innovate and create new applications and services that leverage the power of connected devices.
Digital Transformation Enabled by IoT
The proliferation of IoT is driving a broader digital transformation across industries, encompassing changes in business processes, customer experiences, and organizational culture:
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: IoT enables organizations to gain deeper insights into customer behavior and preferences, facilitating personalized interactions and tailored offerings. From smart retail stores to connected vehicles, IoT-driven experiences enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Operational Efficiency: By leveraging IoT data and analytics, organizations can streamline operations, automate routine tasks, and optimize resource utilization. Predictive maintenance algorithms prevent costly equipment downtime, while real-time inventory management systems ensure optimal stock levels and reduce overhead costs.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: IoT empowers organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time data and actionable insights. From optimizing supply chain logistics to fine-tuning marketing strategies, data-driven decision-making drives competitive advantage and business growth.
- Agility and Innovation: IoT fosters a culture of innovation and agility, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing market dynamics and emerging technologies. By embracing IoT-driven innovation, companies can explore new revenue streams, enter untapped markets, and stay ahead of the competition.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its transformative potential, IoT implementation poses various challenges and considerations, including:
- Security and Privacy Concerns: The interconnected nature of IoT devices increases the risk of cyber attacks and data breaches, necessitating robust security measures and regulatory compliance frameworks.
- Interoperability and Standards: The lack of standardized protocols and interoperability between IoT devices can hinder seamless integration and data exchange, requiring industry-wide collaboration and standards development.
- Scalability and Complexity: As IoT deployments scale up, managing the complexity of interconnected ecosystems and data flows becomes increasingly challenging, necessitating scalable architectures and robust management tools.
Conclusion: The Internet of Things represents a transformative force that is reshaping industries, optimizing processes, and enhancing our daily lives. With its wide-ranging applications and numerous benefits, IoT has the potential to drive unprecedented levels of efficiency, convenience, and sustainability. However, addressing security, privacy, and interoperability challenges is crucial to unlocking the full potential of this technology. As IoT continues to evolve, we can expect a future where our world becomes increasingly interconnected, intelligent, and data-driven, opening up a world of possibilities for innovation and progress.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

Artificial Intelligence (AI) : 1 : Unleashing the Power of Intelligent Machines
Introduction:
A sector that is rapidly bringing changes will be technology. It is so advanced now, that has brought revolutionary changes over the years. When I say revolutionary advancement in technology it simply means advancement in artificial intelligence. AI has already surpassed boundaries that were once considered unattainable. At present AI is the most used term across various industries. In this article, we will explore different aspects of AI including its key components, applications, benefits, and potential challenges.

1. What is Artificial Intelligence?
The term artificial intelligence refers to machines that are capable of performing human intelligence. Fundamentally, it can think, learn, adapt, and solve problems like a human being. There are a few branches of AI, which include machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, fuzzy logic, and robotics. The advanced features of present artificial intelligence have already brought changes in various sectors including healthcare, finance, and E-commerce.
To know more about AI, keep reading the article.
2. Key Components of AI
AI can perform a task based on your input, an input can be in any form, it could be a text, speech, or even an image. After careful processing of your input, an AI will be able to provide a result for you. Understanding the components of AI will give more insights into its working mechanism. These are the major AI components.
2.1. Learning
Humans learn to improve their skills, and just like that an AI also needs to learn to produce adequate outcomes. In order to improve the performance of an AI-driven technology, an expert may rely on different techniques. Two of the commonly used techniques include trial-and-error and rote methods. These techniques will optimize the problem-solving potential and vocabulary of an AI.
2.2. Reasoning
In the case of an AI, reasoning is simply its ability to draw inferences from the information at hand. The inferences are largely divided into two, they are known as inductive and deductive reasoning. Inductive reasoning is a logical process that involves drawing general conclusions from specific information on the other hand deductive reasoning is drawings from general principles to specific ones.
2.3. Problem Solving
A large amount of data is the foundation of AI technology and its problem-solving potential largely depends on these data. The problem-solving component of an AI involves resolving different problems through a series of different steps.
2.4. Perception
AI perception involves analyzing and interpreting the environment using the sense organs. At present, self-driving cars use perception as a component to moderate speed.
2.5. Language Understanding
AI can distinguish different types of languages just like us. It is one of the widely used components in AI.
3. Different Areas of Application
At present many industries use AI-based technologies to improve the efficiency and performance of various tasks. The following are the top sectors that use AI-based technology.
3.1. Healthcare
The healthcare sector can utilize AI in various fields. New AI-based systems are capable of analyzing medical images like X-rays and MRIs to draw accurate diagnoses. It can also help to predict diseases like cancer which can ultimately lead to earlier detection and treatment.
3.2. Finance
The sector uses AI to recognize fraud practices and new investment trends. The AI-driven system can predict potential fraudulent activities by studying suspicious actions. It can also analyze large amounts of data to draw accurate trading decisions.
3.3. E-Commerce
AI’s ability to predict past behaviors and preferences of customers will help e-commerce platforms to offer personalized recommendations. Amazon and Netflix are great examples of effective implementation of this feature. In order to optimize personalized marketing, AI will process large amounts of data as well. It will help to predict the product demand and reduce waste as well. Chatbots and voice assistants can also improve customer’s shopping experience.
3.4. Autonomous Vehicles
The automobile industry has already given way to AI-powered autonomous vehicles. Tesla and Waymo are the two greatest examples of AI-enabled vehicles. These autonomous vehicles can navigate through roads without any issues, they can even understand the traffic signals, and avoid any kind of obstacles found on the road. Adaptive cruise control, lane departure warnings, and automatic braking systems are other AI-based features found in autonomous vehicles. Besides these features ensure utmost safety for a driver as well.
3.5. Natural Language Processing
Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are well-known virtual assistants that can process voice commands and respond accurately to user queries. Other AI technologies like Google Translate can help people to communicate effectively in real-time. It can also help businesses to grow by analyzing customer feedback and drawing conclusions regarding customer sentiments. Likewise, AI-powered chatbots can also be a great help in improving customer service.
3.6. Education
AI can bring revolutionary changes in the education sector. Personalization is a new learning strategy that refers to the customization of learning materials based on the challenges of the students. In this case, an AI system offers great help. It will help adapt new learning materials based on students’ challenges which can result in enhanced learning outcomes.
Some AI-powered tutors provide quick feedback to students. These types of technology optimize student support and also offer simplified teaching strategies for learning difficult concepts. AI also has the potential to offer an automated grading system.
3.7. Entertainment
Advanced AI can generate music, art, and stories in other words it can transgress the boundaries of creativity. However, the invasion of AI into the creativity sector is still a topic of discussion. AI-driven technology in gaming platforms can improve the gaming experience by adapting the gameplay to create different dynamics.
3.8. Agriculture
Artificial Intelligence can bring advanced changes in the field of agriculture. This field can make use of AI to elevate cultivation techniques to a progressive level. AI-powered autonomous tractors, drones, and other types of advanced machinery used for traditional farming improve the quality of the whole cultivation process. AI can monitor crop health, predict the weather, and even optimize the use of resources.
3.9. Energy
Now you are familiar that AI can process an excess amount of data just to study the consumption patterns, study of energy consumption patterns in the Energy sector can optimize energy use and distribution across smart grids. To reduce repair costs and power outrages, AI can be used in passing information regarding the failure of energy types of equipment. These AI-enabled systems are so clever that can even predict the changes in weather patterns which will ultimately improve the efficiency and productivity of renewable energy sources like wind and solar power.
3.10. Human Resource
Screening resumes and conducting interviews are long and hectic processes. AI can help to screen a huge number of resumes and select suitable candidates by identifying keywords. It can even help to conduct personalized training programs and interviews.
3.11. Security and Surveillance
In the security and surveillance sector, AI systems can monitor and identify individuals in real time. It can also detect suspicious activities and objects. AI applications in the sector will help reduce crimes in the cyber world and the real world.
These are some of the top sectors which use AI to improve their efficiency and productivity. In the coming years, you may see further advancements in the field, it may also get implemented in other fields as well. Now you the application of AI in different industries. So let’s delve into the other important sections of this article.
4. The Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
The ability to solve complex problems, the potential to make accurate decisions, and unprecedented opportunity for innovation have made AI one of the transformative technologies of the modern world. It has already established an upper hand in almost all top sectors.
Now AI has achieved advanced capabilities that were once considered unattainable. However, AI still poses a lot of challenges but when it comes to improved productivity and efficiency the technology can offer immense benefits. Given are some of the benefits of artificial intelligence.
4.1. Increase Productivity
One of the top benefits of AI-based technology is its ability to improve productivity and efficiency. As mentioned before, various fields have already adopted AI to enhance their performance in different areas.
The ability to analyze large amounts of data in real-time, making quick and accurate decisions without being tired and without making any delay. This feature of AI will eventually lead to an increase in productivity and efficiency.
AI tools like machine learning algorithms can even process different sets of data to identify patterns and trends that are difficult for humans to detect. It can also improve a company’s execution of tasks and operations. Moreover, AI will also reduce resource waste and optimize decision-making across different hierarchies.
4.2. Automation of Tasks
Automation of repetitive tasks can improve the efficiency of workers in a firm. Doing a repetitive task can be quite boring and soul-killing for many. If AI can take over these mundane tasks it can automatically improve the creativity and working quality of a human. This automation process can be a great help in industries like customer service where AI chatbots can answer repetitive questions.
AI- technology can also offer help in data entry, invoice processing, and other administrative tasks. This will effectively eliminate the need for human intervention and reduce any chance of errors. Beyond these capabilities, AI has the potential to monitor crop health, irrigation, and weather patterns making ways for effective farming strategies.
4.3. Improve Decision-Making
Since AI can process large amounts of data at a higher speed, it will improve the decision-making process in sectors like finance and e-commerce. AL algorithms can analyze market trends and predict prices and investment trends. Beyond this, the AI’s ability to diagnose conditions simply by examining images can revolutionize the field of healthcare as well.
4.4. Addressing Global Issues
The world faces a lot of challenges at the moment. AI can lend a hand in addressing many of the global challenges like climate change, resource management, and public health. Monitoring the environmental changes with the help of an AI will help to reduce climate change to an extent.
It can also be used to optimize energy usage and help reduce carbon emissions into the atmosphere. Studying the weather pattern with the help of an AI can further advance the field of renewable energy as well.
During an outbreak, AI can play a vital role by tracking the level of disease outbreak, We have already witnessed what AI can do during a pandemic in the times of Covid 19 outbreak. AI systems were used in these times to track disease outbreaks and to make predictions regarding the spread of illness.
4.5. Economic Growth
AI can lead to enhanced economic growth by creating new jobs. Generative AI can actually increase the demand for new professionals. Obviously, AI is going to expand in the coming years, it will definitely increase the demand for professionals with expertise in AI development, machine learning, and data science. It can offer career growth and learning opportunities to individuals.
Apart from these major benefits, AI can offer other advantages such as personalization in the field of education, improvement in the field of healthcare, enhanced public safety, reduced crime rates, and effective establishment of law and order. Eventhough the field of AI has a lot to offer, it still faces a lot of challenges in the present stage. Let’s explore that in the coming section.
5. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Of course, AI is one of the influential advancements of the modern era. It offers enormous benefits in various sectors and it can even make our life more simple. However, AI holds a significant amount of challenges and ethical considerations. Following are some of the disadvantages of artificial intelligence.
Biased Information – Some of the data fed to the AI may contain biased information which can ultimately result in a biased outcome. A possibility of such bias is more prevalent in sectors like hiring, lending, law enforcement, and healthcare.
Lack of Transparency – The lack of transparency in the world of artificial intelligence is always a matter of concern. Understanding the nuances of the decision-making process is valued in fields such as healthcare, law enforcement, and finance. But a large part of AI’s decision-making process is hidden so this can be a matter of concern at so many levels.
Job Displacement and Economic Impact – AI-driven automation may lead to the displacement of various jobs which particularly involves repetitive tasks. Automated AI can easily and effectively replace humans in jobs that heavily rely on repetitive tasks, especially in customer service, manufacturing, and transportation. Automation in certain jobs can largely affect low-skilled individuals. Besides, the non-creation of new job opportunities is another huge concern caused by AI.
Privacy Concerns – AI uses excessive amounts of personal and sensitive information for its advancement. Collecting and storing individuals’ private information is highly concerning. Facial recognition technology, AI-driven surveillance systems, and data-tracking technologies break the rule of privacy to a great extent.
Accountability – Decisions made by an AI have no accountability. If anything goes wrong after implementing a decision made by an AI, no one can be held accountable for it. If an automatic vehicle makes a mistake, who is responsible for the mistake committed is still a question. According to the current scenario, no one can provide an answer to it. Framing clear guidelines and legal frameworks will help assign some responsibility if an AI makes a mistake.
The exploitation of AI – AI has loopholes that can open doors for various types of exploitation. AI can be used to launch cyber attacks or misinformation campaigns. The development of automatic weapons is another great fear.
Global Inequality – When developed countries acquire more advanced technologies in the field of artificial intelligence. The underdeveloped and developing countries may struggle to keep up with the pace because they lack access to advanced technology. This may result in a digital divide which can eventually lead to economic and technological gaps between nations.
It is evident that AI raises a lot of concerns and challenges. Ethical considerations and framing new laws are crucial to mitigate the severity of these issues. It will help to ensure equality and the development of responsible AI technologies in the future.
6.Conclusion
In conclusion, artificial intelligence has certainly brought significant differences in the working of the world. All these advancements achieved by the technology were able to alter the way people viewed AI technologies before. So many sectors like healthcare, finance, education, and many more make use of its features to improve productivity and performance.
There is no question that AI will continue to expand in the coming future as well. However, the rapid growth in AI technology raises some concerns regarding its transparency, accountability, collection of data, and usage of sensitive information. Implementing new laws and formatting new guidelines can help to alleviate these issues to a great extent. Apart from this advanced AI will continue to thrive and simplify people’s lives in the future.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology

How IT Conferences Supercharge Your Connections
Introduction
The IT environment is a competitive system that is full of change and is characterized by continuous innovation. Maintaining a place for one’s enterprise in this constantly evolving world is not only a nice thing to do; it is necessary. IT conferences turn into the lights of knowledge, innovation, and networking, becoming a rich source of success for organizations and key points of interest for professionals. These meetings convene a wide range of players from industry pioneers and up-and-coming business people to cooperate, gain knowledge, and get inspired. In this subsystem, through this paper, I sought to uncover how these realized advantages of IT conferences are truly within a range of possibilities that promise change and growth.
The energy at IT conferences is electric!
Everyone’s so passionate about technology, it makes connecting effortless.
Expanding Your Professional Network: Between the Episodes of Extremes
Conferences are business-oriented and the greatest specificity of PT and IT conferences emanates from the fact that one can potentially meet everyone. Networking is a crucial factor that Fabrikam Enterprises CTO, Mark Smith stresses in referring to the numerous opportunities for interaction. Modern businesspeople encounter each other not only during meetings and conferences but also during downtime, coffee breaks, and other formal and informal networking opportunities.
Besides, all IT conferences are open to the public, and this encourages the participation of large numbers of people with divergent opinions. This is beneficial in enhancing the essence of networking since this opens opportunities and avenues for new associations. Research by the International Data Corporation (IDC) further supports the outcome found in networking.
From their studies, it is possible to conclude that personnel with dense networks have higher chances of getting a job and career promotion. IT conferences are effective platforms for one to build and manage his or her networks since everyone has wisdom and experience to offer. This knowledge makes them ready to work in the chaos of the IT environment and advance in their respective career paths.
The success of Networking at an IT Conference
Let me offer an example from the real life. One of the incidents is the story of Sarah Jones who is a software engineer working at a start-up company. While attending a networking session, she got acquainted with David Lee, a Cloud Architect in one of the developing high-tech gigantic firms. Concerning the use of containerization technology, they also opined and agreed on the matter. As a result of this interaction, Sarah got to know more about the new trends in the service of container orchestration that is used by David’s company.
Thus, David got an understanding of the issues related to the adoption of cloud technologies in start-ups. This fate brought them to collaborate between their companies for a longer period. As seen before, David came in handy to help Sarah and her team design an efficient cloud infrastructure that is also efficient in cost. This example is a perfect illustration of the networking process with other IT gurus during conferences, the growing exchange of experience, and ideas, and the creation of successful business contacts that can positively reflect on the individuals and organizations.
Learning About Bleeding-Edge Tech: Sustaining Innovation Advantage
Corporate evolution and the ever-changing market landscape heavily reliant on contemporary trends require one to catch up with the current changes. ITS conferences provide the best solutions and technologies while immersing the attendees in the world of innovations and ideas. According to Lauren Kim, the Chief Information Officer of MediaCorp, these events have played a dramatic change in the thinking and direction of the organization with the promotion of creativity and risk-taking.
While basic IT conferences include; speakers and presentations from industry leaders, the actual tactical learning experiences include; toolbox sessions, technical sessions, exhibitions, and demos. Delegates receive valuable insights about novel technologies such as artificial intelligence, let’s say, blockchain and edge computing; they come to learn how those can be applied in their firms. Besides, vendor exhibitions allow the participants to interact with solution providers in the course of the event. It allows them, in a way, to test the latest concepts and, possibly, establish bilateral cooperation that will bring their organizations to the next level.
Up-Skilling at An IT Conference- A Catalyst of Innovation
For instance, Michael Brown is a network security specialist for a financial firm. On one day of the trip, Michael was able to take a workshop on the new threats on the Internet and protection measures. He proposed to explore areas associated with newly emerging techniques utilized by cybercriminals as well as social engineering and zero-day attacks.
These understandings enabled Michael to find gaping holes in his organization’s current security position. After coming to work he met with the IT security team to share the findings and suggestions he had made. This stimulated the need to develop a more effective security platform to improve their capacity in the provision of secure means to consumers. This case signifies how the upskilling at IT conferences avails opportunities to enhance the skills of the personnel, and in turn, create solutions that help organizations to grow premier.
Reviving Insights in Your Organization: Overcoming the Barriers, From Conference Halls to Actionable Strategies
Such activities as post-conference debriefings, knowledge-sharing meetings, and collaborative workshops enable the working teams to bring ideas into practice and introduce changes. Desk 2, for instance, shows that knowledge exchange mechanisms realize the enactment of a culture of innovation and improvement.
Another core success factor in the implementation of new ideas and initiatives proposed and discussed at IT conferences is the support from the organizational leadership. When exposing the possibility and benefits of advanced technologies, more advocates are made, and change in organizational approach is promoted. According to findings by Harvard Business Review innovation is crucial for organizational performance. According to their research, they identify that firms that invest in innovation do better than their competitors regarding revenues and market value. Thus, integrating new ideas and technologies into an organization’s environment allows it to achieve competitive advantage, improve performance, and provide greater customer satisfaction.
Maria Garcia is a marketing manager at a retail company and recently attended the conference on digital transformation where she returned to the company charged. She took her team out for a knowledge-sharing session where she presented new patterns in e-commerce and concerns about omnichannel marketing. Maria also created a PowerPoint presentation where she explained to the executive team the importance of implementing these emerging technologies to enhance customer, sales, and organizational satisfaction.
She backed all her points with facts that she collected from the conference and this was quite impressive to leadership. This led to the provision of funds for putting into operation a digital transformation project in the organization. This paper therefore seeks to establish how the dissemination and promotion of stored knowledge can help in actualizing what is learned in conferences into positive impacts in organizations.

Maximizing Conference Value:
A Strategic Plan For participants to benefit from social networking services during the IT conferences, they need to follow a certain plan on how to actively participate and engage in activities. Thus, before paying a visit, it is important to be quite precise about the expectations. Both sets of objectives should apply to the goals of the attendee in their chosen career as well as their organization’s strategic plan.
This means that conference attendees have an opportunity to plan for major sessions and workshops likely to assist in the achievement of the above objectives. Another important approach here relates to the engagement of an organization in networking activities. This may involve going to a networking reception, participating in Group discussions, or scheduling a one-on-one session with other professionals or, potential clients. They can therefore enhance the experience as made available by the organizers of the conference as described in the following sub-sections.
That is why the application of mobile conference apps has such benefits as the possibility to build one’s timetable, exchange opinions with the other participants, share something with them, as well as to communicate before, during, and after the conference. In addition, often the organizers of the conference additionally distribute such things as presentations, records, and white papers which can be used by the participants after the conference. By taking advantage of these resources, attendees can continue to learn and grow long after the conference has concluded.
Organizing Experience Using Digital Tools:
In terms of organization, using digital tools helps to strengthen the experience of a conference. For instance, consider John Lee, a software developer who encountered the concept of cloud-native development at a conference. Before the event, John used the feature of the conference app to build a custom agenda for him, and among the topics he chose, there were sessions on containerization technologies and microservices architectures, which are currently relevant to the group he works with. John used the note-taking facility of the app also and was very much engaged during the conference and made comments.
After the conference, he took notes and what he considered relevant responses for his working group during a project meeting. John also ensured that he got to use the conferencing online resource library where people make their presentations available since he could not be present physically for some of the ones being conducted. This confirms and underscores the importance of the enabling technologies for enhancing the extent of knowledge acquisition from the conferenced events and sharing within teams.
The Evolving Landscape of IT Conferences: Leads, Marketing Opportunities in The Time of Covid-19
Aim To understand the status quo and the current state of trends in IT conferences taking into account the role of online conferences that have recently gained special popularity. There are several advantages of virtual conferences, such as it being possible to reach out and organize the conference from any part of the world hence making it very accessible; One cannot consider the cost factor in organizing a conference when they are going for virtual form of conferences; A conference in virtual form is best for a worldwide audience since nobody will be restricted by geographical barriers.
They also allow organizers to vary exclusive tools and types of content, such as webinars, live question-answer sessions, or archives with content available at any time.
Of course, virtual conferences have certain advantages that behave differently than physical ones and which cannot be emulated completely. Despite that, the energy that traditional conferences provide, the chance to meet people by accident, and the possibility to discuss things face to face are seen as equally important. Yet, the concept can be tackled head-on through Hybrid conferences that is, meetings that have both online and offline components. Online invitations and proper mixture of online mode with traditional format therefore should be used by IT conferences so that they can continue to enable professionals as well as organizations to exploit the changes of the new IT world.
Hybrid Conferences Provide Levity and Expand the Multitude
Reflect on a highly popular cybersecurity event that in the past invited participants from all around the world. In this case, the organizers noted an increasing trend of virtual participation and thus, chose to combine the format. This enabled cybersecurity personnel who were based off-site to listen to keynotes, join live question-and-answer sessions with industry leaders, and, watch recordings of technical sessions. At the same time, in-person participants enjoyed the specifics of networking, meetings face-to-face, and the creative atmosphere of the physical convention. Thus, this hybrid approach managed to address a larger audience and provide the major value of the traditional conference format.
Finally, it has been found that IT conferences exist as active throbbing forums of learning, networking, and creativity in the constantly emerging technological era. Since 1996 these four events have enabled IT professionals and organizations not only to better understand the major trends and challenges in the fast-growing IT industry but also to achieve their personal and organizational breakthroughs. It can be expected that IT conferences will remain ever-evolving and will incorporate methods of online and offline events for participants from all over the world. Engaging and utilizing the possibilities of these events, IT specialists will be able to become leaders and actively influence the further development of the constantly evolving IT world.
A research proposal toward a qualitative and quantitative understanding of where IT Conferences are headed
The future of IT conferences promises to be a fascinating tapestry woven from several key trends. The future of IT conferences promises to be a fascinating tapestry woven from several key trends:
1.Continued Growth of Hybrid Formats: A fantastic context is created by the accumulation and interaction of the elements of both the real and the magical worlds; Muhammad’s dream is the result of a direct juxtaposition of the two worlds. These are for discussing a hybrid way of holding the conference, which is less risky and has a greater potential in terms of attracting the audiences and ensuring access. Hybrid conferences, where some of the events take place online and others in physical space, will likely become even more common in the future.
This approach helps the way that this pleases all of the attendees allowing the geographically challenged or financially restricted professionals to be as active as those who can travel downtown. Synchronous hosted live sessions, such as keynote presentations combined with synchronous webinars and on-demand libraries of stored content allow for global knowledge sharing from a distance. On the contrary, the physical presence gives the possibility of direct communication that enhances relationships, new group encounters, passion for the meeting, and numerous collaborations in person. Meetings and conferences that have adopted the use of technology will continue to break geographical barriers as a result of hybridization.
For instance, let us contemplate an annual global conference on Artificial Intelligence. Which in most cases only catered to the few practicing professionals within that one geographical area. However, by opting for such an organization of the conference, the organizers attracted significantly more attendees than if they had limited themselves to one method exclusively. This proved to be beneficial in a way as it allowed AI researchers and developers from across the world to join virtually and interact with other participants, listen to keynote speeches by industry greats, ask questions to the speakers, and join live Q&A sessions, as well as access an extensive technical workshop library.
As for participants who attended this event in person, they enjoyed unique and inestimable experiences; on the one hand, attending the event allowed them to make cross-cultural connections and enhance their interpersonal network, while on the other hand, they were able to generate new ideas by directly interacting with other participants. This hybrid approach ensured an effective reconciliation of geographical barriers and allowed the creation of an AI community that is comprehensive and connected on a global level.
2.Focus on Interactive Learning: People are not only consumers. Let us now examine this idea further by talking about non-consumer-focused aspects of media use. It can be assumed that in the future, vastly more attention will be paid to the implementation of activities that teach people concepts and ideas that cannot be transmitted merely through lectures.
3.CH 2: Interactive elements like gamification can efficiently turn a boring process of learning into an interesting and fun process. The latter was readily identified through opportunities such as engaging in one of the cybersecurity simulations in which participants try to identify and counter cyber threats or attending a cloud computing workshop in which attendees work collectively to build and apply containerized applications in an actual environment. Thus, live coding sessions can be an insightful way of revealing the distinctive approaches and strategies of professionals. It is a common practice for referring to knowledge exchange and teamwork purposes the collaborative workshops that stimulate the IT students to come up with creative solutions to actual IT issues.
4.Leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI): Personalization and the Use of Professional Networks Based on the discussion, it emerges that AI can go a long way toward enhancing the personalization of the conference. Visualize an app situated at a conference updated by your professional identity data and your previous activity as a user. This way, this “smart” app can suggest matching sessions, workshops, or other meeting opportunities that comply with its user, both in the professional and personal growth sense. Besides, using AI it is possible to find like-minded people. Future-designed attendee characteristics and preferences could be suggested as potential networking matches, thereby creating fruitful, chance meetings and contacts.
5.Focus on Emerging Technologies of business: As the business environment continues to change at the tempestuous pace that Earling (2008) indicated it was, organizations cannot afford to be complacent. IT conferences will also remain as popular as before as they provide an opportunity to get familiar with innovations that have not found their way to commercial use yet. Picture yourself getting to know the idea of quantum computing and the finance industry disruption or the workshop on ethics and artificial intelligence.
Thus, conferences educate the attendees on what new thoughts leaders in the industry are thinking about new technologies through panel discussions and allow one to learn what is emerging in technologies in a certain field which prepares one’s organization to adapt to the new developments in Information technology.
6.The Rise of Niche Conferences: The last category which is also an essential segment for furniture stores is that of the clients with specific requirements or needs. While there is a move towards large conferences covering large themes of IT, the same causes might also bring in smaller meetings confined to certain areas in the general IT spectrum. These specific events provide mechanics explorations into distinct technologies to develop discussions and share information among an inspired collective of professionals.
For example, a specific event dedicated to the blockchain industry can address such issues as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-homogeneous tokens (NFT), Web3, etc. Such specialized conferences give a chance to professionals to discuss issues with other people and find common solutions, which leads to the development of specific technology domains.
Thus, it will be vital for IT conferences to adopt these trends and encourage learning and innovativeness to sustain their importance in the ever-evolving IT environment. The technological environment today is constantly evolving and this underscores the need for IT professionals to learn and be ready for change.
IT conferences are valuable for a company as those events allow people to gain new knowledge, find new partners, and discuss recent tendencies. They provide a unique opportunity to:
1.Expand Your Professional Network: Create useful professional contacts with people from the same business as you, researchers, and possible partners. Be able to build networks of contacts that may later on secure one an opportunity to work, form the business, or share ideas with others.
2.Gain Insights into Cutting-Edge Technologies: Pursue updates in technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, cloud computing, and other additional fields. Discover what these technologies can mean for your organization and how to apply them.
3.Learn from Industry Experts: Get involved that sessions that are presented by some of the biggest personalities and influencers. Learn from their experience and views of the world in which they live.
4.Spark Innovation: Discuss new concepts and strategies with coworkers and partners that solve existing IT issues. In this regard, foster a culture of innovation in your organization.
5.Shape the Future of IT: Participate in conversations and debates regarding the set ethical and social aspects of new technologies. Help influence the way IT outwardly looks and operates in the future.
If you have not yet done so I’d recommend going to at least one IT conference of your specialization. Here are some additional tips to maximize your conference experience:
1.Set Clear Objectives: To achieve this, decide on your objective when you intend to go to the conference. What is it that you expect to get out of here, either by benefiting from what others have to say or simply as a result of your interaction with other participants: What would you like to get out of here? It is imperative to attain clear objectives because it will help determine which sessions and workshops are important.
2.Develop a Personalized Schedule: Take full advantage of the conference applications and materials to create a program as far as your goal and passion are concerned. Major in things that push you to the next level and take you out of your comfort zone.
3.Actively Participate: Get involved by getting into discussions, asking questions, and making connections with other people who are present in the meeting. Take full part in that whole process as a learning experience: do not simply watch and listen.
Follow Up After the Conference: Collect all the business cards of the persons you have met at the conference and also take note of people you have previously met online. Make sure to put into action what you acquire at the conference within your organization.
The Ever-Expanding Universe of IT Conferences
The concept and popularity of IT conferences are seemingly ever-evolving and growing rapidly in the present epoch. IT conferences keep increasing in numbers as well as their varieties represent a rich opportunity for IT professionals regardless of their experience level. Here’s a glimpse into the different types of conferences you might encounter:
1.Megaconferences: These are big events that can gather thousands of people and the majority of the sessions are related to IT subjects. Continuing the topic, they represent a rich source of ideas, innovative products, and contacts.
2.Industry-Specific Conferences: These conferences are industry-based IT sectors like information security, the cloud, and artificial intelligence to mention but a few. It gives a focus to a certain topic and helps to establish detailed dialogue and further the sharing of information among a group of experts.
3.Vendor-Sponsored Conferences: Technology firms particularly organize meetings where they exhibit and explain their products and services. These events are rather useful in terms of gaining certain, narrow-scope information about specific technologies and are also useful in terms of allowing direct interaction with representatives of the vendors involved.
4.Regional Conferences: Regional conferences are also more localized where the meeting is organized within a certain geographical region thus the closeness that comes with the meetings. Some of them act as networks that bring together specialists in a given area and let them discuss the tendencies of the local market.
5.Virtual Conferences: Virtual conferences remove the physical space constraint in that one can attend the conference from any part of the world. It has the advantage of providing cheaper and more flexible means of being able to have access to quality learning.
Conclusion: A Growth and Innovation Enabler
Therefore, IT conferences remain the benchmarks for creating the path to great career development and progression in the competitive IT market. Thus, the given events help professionals and companies share information and get new ideas and the experience of their colleagues and peers as well as discover new technologies and approaches in the constantly evolving digital world. Thus, attending IT conferences will remain relevant and develop continuously, combining online meetings and live events for participants from all over the world. Thus, IT professionals may enhance their positions as active beneficiaries and leaders of the ever-evolving IT sphere by experiencing the change personally at the events listed above.
Follow Me for regular Updates on LinkedIn; Twitter; Facebook & Instagram for all Technology Articles
View My other Blog posts Here
Join Us on GRK Connect @ Telegram; Discord & LinkedIn Groups for Discussions on Technology


















